Things are never what they seem and are not what they appear. Such paradox is evident in business transformation and strategic management when focused planning, an essential aspect of the process, becomes a disadvantage. Therefore, one must wonder when strategic planning becomes unadvisable.
There is never a time when strategic planning is not advisable, as it is the lifeblood of every organization and an indispensable aspect of success. Instead, business and corporate entities are advised to avoid common errors in creating and implementing focused plans, including failed or unsuccessful ones.
Even though strategic planning is designed to advance most businesses, there are weird times when it appears to be more of an encumbrance than a catalyst for increased return on investment. Therefore, this article covers insight into what nullifies focused planning and what business owners can do differently to reverse the ill effects of a failed strategic plan.
When Do Businesses Neglect the Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic or targeted action plans are not worthy of implementation when they fail due to several structural reasons. Examples of such structural inconsistencies include but are not limited to:
- When there is a fundamental error with the overall blueprint.
- When the plan is cumbersome, probably with too many strategies and KPIs.
- Problematic budgeting and resource allocation and general challenges with the planning process.
What Are the Phases Required To Validate Successful Strategic Planning?
An effective targeted business design must pass through the three phases of strategic planning to be valid. Here they are:
The Intuitive Phase
The intuitive phase is the first phase for successful targeted designs. It involves the emotional aspect of the business, which answers questions about the company’s essence of being.
Examples of such intuitive questions include but are not limited to
- Who are we?
- What do we stand for?
- Who are our target audience or customers?
- What are our values?
- Where do we expect to be in the next couple of months or years? Etc.
The Analytical Phase
The second phase is the analytical phase which involves a more logical aspect of thinking. It functions as a support system for the intuitive stage, which is more emotional. Essentially, the analytical step is more future-oriented and tries to determine the company’s place in the larger market.
It is akin to thinking outside the box and considering the business as a separate entity existing within a larger entity, the marketplace.
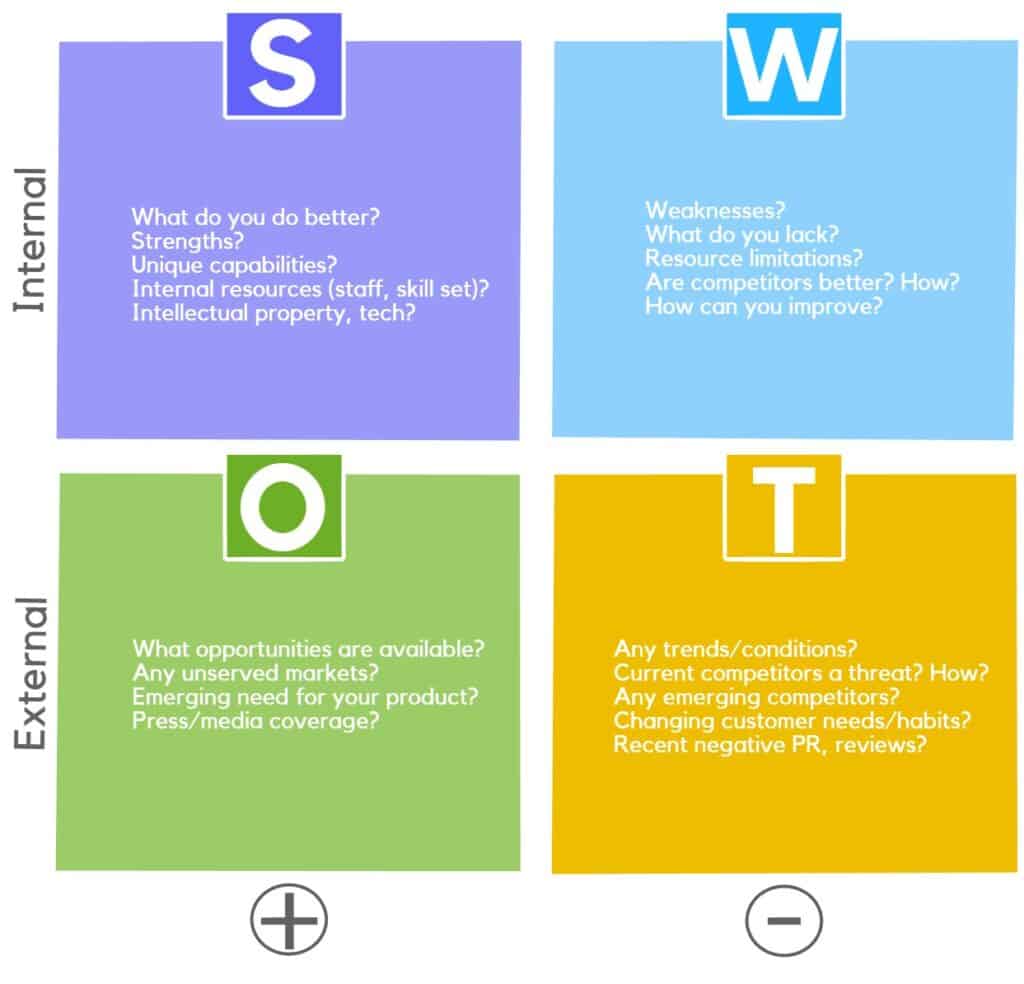
At this phase, analytical processes like the SWOT analysis become useful for determining the establishment’s overall course of action.
Examples of topics of consideration during the analytical phase include but are not limited to:
- Business strengths and weaknesses
- Customer relationship management
- The place of technology in business
- Market trends and their effects on the business, etc.
The Operational Phase
The operational phase is the third phase of validating a business design. It includes all practical and specific actions needed to support the business organizers’ intuitive and analytical thought process.
Essentially, this phase is more practical-oriented, where all thoughts and business designs are implemented to see their outcome. It also includes resource allocation and utilization, including process appraisal to chart the organizational milestones against preset targets.
Examples of Common Challenges With the Strategic Planning Process
Every business process is not without its fair share of challenges, and strategic planning is no exception. Interestingly, the problems with targeted business designs serve as measurable indices for any establishment to measure its progress level.
Below are four critical challenges associated with targeted corporate plans to help bolster your understanding of what solutions to implement.
No Particular Authorship
Targeted business designs do not have a specific author, making it difficult to have someone to hold responsible for the plan. In essence, it lacks ownership since it has a decentralized structure. The reason is that strategic planning is often cross-departmental and cross-functional and, without extreme precautions, easily degenerates into a disjointed design.
Weak Communication Structure
An effective plan is non-existent without adequate communication among the stakeholders. Similarly, target business designs lack effective communication because of the likely long chain of command and authorship problem.
When no specific entity is responsible for the ownership, communicating actionable steps within the business plan becomes difficult. However, most companies have recently incorporated several digital processes besides emails to maintain communication.
Inclusive Input
A general and holistic input from all aspects of the organization is paramount for an effective strategic planning process. The reason is that it gives a voice to all aspects of the business where various representatives contribute their unique elements toward achieving organizational goals.
The inclusive input leads to a better and more stable alignment of the company with its overall objectives.
Retarded Adoption
Most establishments struggle with adopting and implementing the proceeds from their targeted planning process. There is no particular reason for the slow adoption, but most strategic analysts blame a depreciating level of motivation.
If team members execute their target business designs with as much enthusiasm as was involved during the creation process, most companies will not need to abandon their strategic plans.
Why Some Establishments Avoid Strategic Planning
Some establishments might avoid strategic planning and even advise against it due to several structural inconsistencies.
Here are a few situations that could stimulate such decisions.
- Insufficient personnel with experience in strategic management
- Poor recognition culture where employees feel unappreciated for their ingenuity and become reluctant to contribute their ideas.
- A consistent lack of cohesion and a team-building approach
- Organizational leadership that is resistant to change and averse to trying new approaches
- Limited budget and organizational resources
- A chronic fear of the unknown
What Factors Ruin the Efficacy of Strategic Planning?
Targeted organizational designs fail due to the following factors or pitfalls:
- Pursuing an overly complex pattern, thus reducing team buy-ins
- When the design lacks relevance of its inability to solve current problems
- When there are ambiguous objectives
- When the plan becomes too expensive and out of budget
- When the procedure is unable to inspire momentum and motivate employees to action
- When the design does not align with organizational goals and objectives
- When the company lacks a recognition culture and accountability
Top Ways To Avoid Challenges With Strategic Planning
Now that you know the common pitfalls of most targeted designs, here is a list of how to prevent or overcome them.
- Create simple business designs
- Have a working document of the process
- Use organizational resources judiciously
- Train your team members
- Use data analytics to create a solid blueprint
- Collaborate with other key players in the industry
- Employ an expert in strategic management if you must
- Review all executed strategies through periodic process appraisals and evaluations.
How Understanding the Pros and Cons of Strategic Planning Creates Better Business Outcomes.
Understanding what you stand to gain or lose from a process helps to bolster your energy for execution. Here are some of the pros and cons of targeted designs.
Pros of Strategic Planning
As cliché as it sounds, nothing happens by chance, thus corroborating the relevance of targeted designs toward organizational success. Here are some advantages of planning in any establishment.
It Sets the Operational Tone for the Organization.
Without a working design, organization members remain at sea concerning their roles and duties. As a result, a plan sets the blueprint for activities within the enterprise and fosters attention to details like organizational objectives, etc.
It Is a Proactive Tool Against Unforeseen Situations
Since the business world is replete with uncertainties and eventualities, every organization requires a targeted design to forestall business uncertainties, like market changes and price actions.
It Encourages Employee Efficiency.
A targeted design is a road map for facilitating the division of labor and delegation. Essentially, delegation creates an opportunity for increased specialization where organization members can concentrate on their tasks to give their best service.
Eventually, the establishment can engender employee efficiency through targeted designs because of the increased control it generates. Employee performance appraisal and evaluation become easier to execute, which leaves room for corrective measures like employee training and development.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Allocation and utilization of organizational resources is a major challenge in most establishments, and it becomes even more problematic without a corporate design. The organizational structure categorizes all available resources and their areas of need which the management can disburse for achieving their goals and objectives.
Increased Innovation Culture and Creativity
Targeted designs set the formula for deciding novel approaches to organizational issues. This way, all ideas pass through the three planning phases to increase their validity. Also, it stimulates continuous out-of-the-box thinking from members to increase productivity.

Cons of Strategic Planning
Some strategic analysts campaign against planning, stating that organizations are better off allowing things to take their natural cause. Here are some disadvantages of focused planning to help you decide what part of the spectrum fits your organization.
It Is Highly Data-Dependent
Planning is extremely data-dependent and requires accurate information to chart the blueprint of any organization. The implication is that erroneous data automatically generates problematic design and can set the company up for failure. Additionally, obtaining reliable data for focused planning can be a hassle and require extreme effort.
It Is Time-Consuming
Time management is a major constraint with focused designs. It can be a huge inconvenience, especially as most targeted methods must pass through the three fundamental phases to become good plans.
As a result, organizational operations can be significantly delayed due to the time required to create a good design. The time-consuming process can cost the business several profitable opportunities.
It Is Capital Intensive.
Curating reliable data for targeted organizational designs can be very expensive. Some establishments might have to hire an expert to assist them with strategic planning, which costs lots of money to maintain.
It Does Not Cover Emergencies.
Nothing is predictable in business, and the increasing uncertainties make it difficult for companies to invest the time required to craft functional designs. Also, these plans expose establishments to external influences like sudden economic policies, technological changes, etc., limiting the organizational ability to accommodate unexpected situations.
As a result, most establishments become rigid and resistant to change because they would rather stick to their old procedures than risk dealing with more uncertainties. The whole idea stems from the thinking that most things planned for are not likely to happen and are merely mental speculations that serve more academic than practical utility.
Here is a table comparing the pros and cons of strategic planning.
| Pros | Cons |
| It encourages economy in operations through predetermined goals | It is data-dependent |
| It fosters superior coordination | It is time-consuming |
| It decreases business uncertainty | It is capital intensive |
| It is focused on objectives by setting the operational tone for the organization | It is rigid and resistant to change |
| It facilitates organizational control and coordination | It does not cover emergencies |
| It increases innovation culture and creativity | |
| It is pre-emptive and proactive for anticipating unforeseen circumstances. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Makes Organizational Target Designs Unnecessary?
Most targeted designs fail because they do not live up to their validity due to a lack of follow-up after implementation. Companies should conduct regular process appraisals and evaluations to keep up with their designs.
Why Do Some Managers Avoid Panning?
Managers who avoid planning often prefer allowing the business to take its natural course. Often, they are resistant to change and would rather remain in their old ways than try new management processes.
What Is the Problem With Having Multiple Strategic Plans in Any Organization?
Multiple strategic plans are difficult to fund and market effectively due to limited resources that must be divided among several project designs. As a result, the constraint on available resources could negatively impact the organization’s overall operations.
Final Thoughts
Several reasons exist why some organizations advise against strategic planning. However, every establishment is unique and would likely make decisions that protect its overall interest. As a result, having sound knowledge of the dynamics, including the pros and cons of targeted organizational designs, helps more establishments with better judgment.