Sometimes, in business, you can encounter situations warranting you to play detective. Businesses, like police investigation, have cases. Problems requiring detailed investigations arise within organizations, and a structured thinking pattern is all you need to unravel the solution to modern business challenges.
A company should use a situation framework only when dealing with business-related problems that are strategic and competitive. It provides the essential structure for conceptualizing business problems that lead seamlessly to solvency by breaking them into cases. Business executives and consultants use it as an analytical tool for situational analysis within the company to boost company performance.
Businesses or companies are always in competition with one another. Also, not all solutions work for every business case or problem. As a result, it is up to every company to devise a working strategy if they must survive the competition.
Let’s discuss situation frameworks and the best time to implement them in organizational management for business transformation.
What Is the Best Time for a Company to Engage a Situation Framework?
Business cases that combine strategic and competitive problems require company executives to employ a business situation framework for a solution. A business situation framework as a tool helps businesses and consultants build cases around strategic and competitive problems.
It provides an avenue for structuring business cases without putting the executives or managers in the uncomfortable position of having to memorize a dozen frameworks. Additionally, it is a derivative of the 3Cs model for business problems in project analysis. They include customer, competitor, and company analysis.
As a result, the situation framework is ineffective for business problems that are not competitive and strategic such as operations problems, supply chain strategy problems, media strategy problems, etc. In other words, business problems that may be strategic but not competitive cannot benefit from using a business situation framework.
Examples of business areas where the business situation framework applies include:
- Entering a new market
- Introducing a new product into the market
- Starting a new business
- Building a business growth strategy
- Business diversification
- Increasing business turnaround metrics.
How Can a Company Implement a Situation Framework for Solving Business Cases?
A business situation framework involves solving business cases structurally. The catch is analyzing business problems from the company’s current issues to improving its performance.
Generally, most business consultants implement the framework by analyzing the customer, competitors, product and company factors to enable them to break into new and competitive opportunities.
Here is how the implementation works:
The Customer Factor Analysis
Understanding your ideal customer and their needs is key in this aspect. As a result, a business consultant or executive must consider some critical factors like specific population (demographics), market specifics, customer and consumer behavior, buying decisions, etc.
More importantly, a clear understanding of your customer needs is vital for achieving customer satisfaction and retention—A major business case among most organizations.
The Competitor Factor
Tackling cases associated with business competitors is essential for attaining the company’s long-term goals. Therefore, common questions business consultants ask during their brainstorming process for competitor cases border around the following questions:
- The market prospect for the company’s product or services
- The company’s share of the market
- The strengths and weaknesses of the company and how they compare to their competitors.
The Product Factor
Most businesses exist to provide a product or service to satisfy customer needs while making a profit. Therefore, the product factor is crucial for the corporate process because it controls the company’s ability to remain in business by providing quality products.
Companies must ensure that their products have requirements to meet consumer or customer needs. This way, they can enhance their marketing by highlighting these unique features.
The Company Factor
Analyzing the business sets the company up for success. Essentially, it involves analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of the corporate organization to enable seamless planning of the entire business process.
How Does a Situational Analysis Facilitate the Formation of a Business Situation Framework for Effective Market Competition?
Like a real investigation, a situation framework requires a situational analysis to sustain and survive business competitions. Situational analysis is a systematic approach to understanding the internal and external factors that affect any corporate entity at a particular time.

These factors include but are not limited to competitors, customers, market environment, and company strength. They allow you to use your company’s strengths to your greatest advantage, including identifying growth areas.
As a result, it involves several phases in strategic planning requiring other analytical tools. It is a process that allows for recognizing new opportunities and challenges.
As a corporate strategy, it covers several other effective analytical processes such as SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, Porter’s five forces, the 5C analysis, and VRIO analysis.
Strategic management involves all methods managers use to analyze corporate internal and external environments to determine their position in the market.
Relevance of Situation Analysis
Situation analysis is relevant strictly for corporate planning. As a result, you should only conduct it to establish the company’s primary strategy or plan. The essence is to create a realistic and objective analysis of your company’s position in the market.
Additionally, the kit helps you better understand other areas of your company and finetunes your problem-solution analysis. This way, you can easily set company goals with actionable execution plans.
Here is a list highlighting the importance of situation analysis in any establishment:
- It helps you identify the nature and business coverage of the firm
- It identifies the strategies for handling all business problems
- It comprehensively reviews current business situations for achieving long-term goals
- It bridges the gap between an establishment’s current and desired level
- It clarifies the blueprint and direction for business activities
- It improves the market penetration rate of an establishment
- Company strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats are exposed.
- It gives a realistic assessment of the business.
- It highlights areas of correction, improvement and further investment for the company.
What Are the Key Perspectives of Situation Analysis for a Corporate Situation Framework?
The business situation framework is so multifaceted that without a clear understanding of some critical aspects of your enterprise, it would be challenging to execute it as an effective business tool.
Here are some key perspectives that apply to situation analysis while trying to implement a working framework.
Product Perspective
Defining what kind of product you want to offer your customers is always helpful. The best method is to analyze your current product and services to improve their quality. You can add extra services or product features to keep your business in the public eye.
Competition
Analyzing your competition is one of the most effective strategies for succeeding in any venture, especially in business. Therefore, performing a situation analysis is incomplete without checking out your competition. It allows you to build your company’s competitive advantage in the long run.
Distribution
Distribution covers how you get your products to customers. Several options exist for product and service distribution, such as dropshipping, affiliate marketing, digital marketing, and omnichannel.
You could also work with physical stores and retail outlets to provide a ready pick-up destination for your customers. Considering your distribution is key to increasing your outreach, including advertising. This way, you can reach, capture and retain long-term customers who will remain loyal to your brand.
The Environment
Internal and external environmental factors influence business success. For instance, internal factors include but are not limited to intercommunication, corporate leadership, etc. In contrast, external factors include government policies, economic factors like the forces of demand and supply, etc.
Most companies perform a stimulus check to enhance their analysis of external environmental factors due to their far-reaching influence on the enterprise.
Opportunities
A clear knowledge of your business’s strengths and weaknesses expose you to the opportunities available to your enterprise. As a result, the SWOT analysis is the perfect window for unraveling every opportunity you can use to increase your organization’s business advantage.
Components of Corporate Situation Analysis for Situation Framework
As earlier stated, the business situation framework is multifaceted. Therefore, understanding the components constituting corporate situation analysis makes you familiar with the exact cases requiring a company to use a situation framework.
Interestingly, situation analysis as a management tool consists of five component analytical methods:
- SWOT analysis
- PESTEL analysis
- Porter’s five forces
- 5C analysis
- VRIO analysis.
Now, let’s look at them individually!
The SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis is arguably the most popular technique in strategic management. It is an acronym for strength, weakness, opportunities and threats. Therefore it is the easiest solution for corporate analytical and strategic cases relating to competition and program/project planning.
SWOT is employed in most establishments at the preliminary stage of strategic management to identify internal and external company factors that can make or mar the establishment’s achievements. It is also useful for generating data for enhancing a company’s competitive advantage.
Although some schools of thought have criticized the strategy, it is undoubtedly the oldest and easiest of all strategic management models.
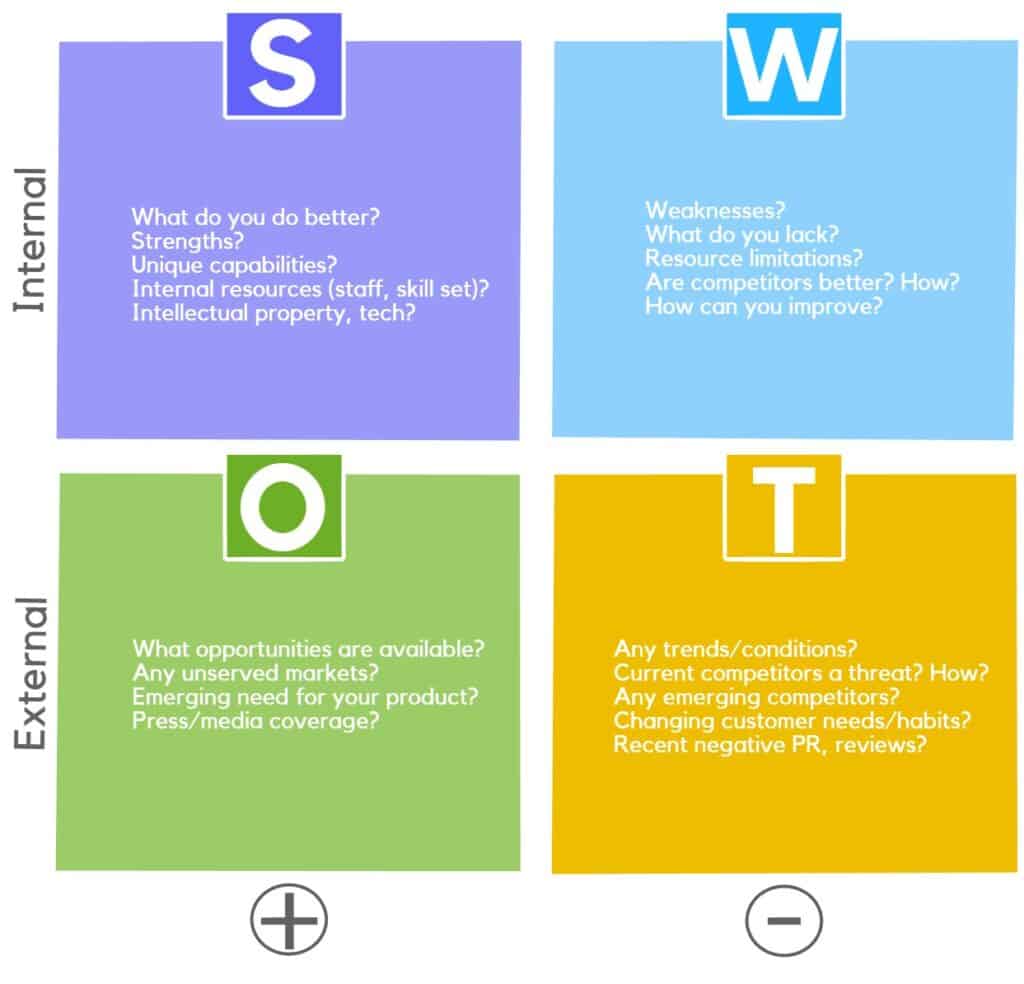
Here is a breakdown of the acronym:
- S for strength describes all company’s best features that place it at an advantage over its competitors.
- W for weakness describes the business’s features or characteristics that place it at a disadvantage compared to other companies.
- O for opportunities include all elements within the company and outside which the establishment could exploit to its advantage.
- T for threats include all environmental factors that could potentially harm the business.
Generally, the analytical results of the SWOT analysis are placed in a quadrant called the SWOT matrix under two major headings: internal and external business factors.
The PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL is an acronym for politics, economics, social, technology, legal and environment. It is another analytical tool for understanding the context within which a business project is implemented.
While SWOT considers external and internal factors influencing your business, PESTEL considers the external factors. As a result, it is very effective as a preliminary analysis before launching the business or as a method of reviewing existing operational methods.
Furthermore, the PESTEL analysis is critical for executing proactive measures in business transformation, like anticipating change and preparing for turbulent economic times.
Here is a table explaining the key factors when running a PESTEL analysis and possible questions to ask during the analytical process.
| PESTEL Components | Key Analytical Factors | Sample Questions for Analysis |
| P for key political factors | Government stability and governance. Public services. Tax laws. War and conflict. | What government laws or policies can affect your company? |
| E for key economic factors | Employment rate. GDP. Inflation. Tax and import duties. Cost of factors of production. | Has the economy experienced any recession or explosion? |
S for key social factors | Citizens lifestyle. Sociocultural norms and beliefs. Income distribution. Education. Entertainment. | What are my target customers? What people or population make up the most significant percentage of available customers? What kind of lifestyle is obtainable in society, and what social trends impact people’s lifestyles? |
| T for key technological factors | Artificial Intelligence. Telecommunications. Social media trends. Digital marketing. Research and development, Inventions. Production efficiency and automation. | What is the biggest technological advancement in my niche? How has technology influenced the market? |
| E for key environmental factors | Human and natural resource management. Environmental pollution. Climate change. Energy reserves. | Does my business activity in any way impact the environment? How does my company support or discourage environmental friendliness? |
| L for key legal factors | Law enforcement and compliance. Judicial proceedings. State laws and legislation. Regulatory bodies. | Are there any regulations binding my business operation? What legal implications affect my business model? |
The beauty of the PESTEL analysis is its emphasis on the influence of external factors on business operations.
Porter’s Five Forces
This is a technique focused on analyzing the competition to eliminate or reduce all threats to your business activities. The technique’s name is derived from the postulation that five forces constitute the intensity of every competitive environment. They include
Substitute Threat
They include the possibility for other products to replace yours. Sometimes, technological advancement or other socioeconomic situations can create a need that leads to substitute threats. For instance, the campaign to drink more water or organic fruit juice as a health advantage can become a substitute for carbonated and fizzy drinks such as coke.
New Competitors
New competitors refer to new businesses or companies entering the market. They are significant because their entry pressures existing enterprises to retain market relevance. As a result, economic factors like costs, price, availability of resources, etc., are affected.
In other words, new competitors are a threat to existing businesses. However, market barriers to entry can significantly influence the rising of these new entrants. For example, a high barrier of entry reduces the threat of new entrants and vice versa.
Established Competitors
Generally, existing companies already have to deal with the rising competition in the industry. As a result of the competitive rivalry, firms resort to expensive and more robust advertising, price slash, etc., to stay ahead of the game. Sometimes, established competitors in the market alter the market ecosystem and reduce productivity.
Supplier’s Bargaining Power
Suppliers wield subtle power over market actions and can hold a firm to ransom with their barging powers. The monopoly of raw materials and price control add to their bargaining power to give them the influence they have. It is also described as the market input.
Customer’s Bargaining Power
Usually, when the customers available are greater than the suppliers, they have the upper hand in an exchange. As a result, the customer’s bargaining power refers to the output factor of the market. Essentially, the availability of options increases customers’ bargaining power by scattering the influence of most businesses in the market.
The Five Cs Analysis
Every business executive using the 5Cs concentrates on the five critical factors affecting their enterprise:
- Company
- Competitors
- Customers
- Collaborators
- Climate.
These factors include internal and external environmental factors influencing business success on macro and micro levels.
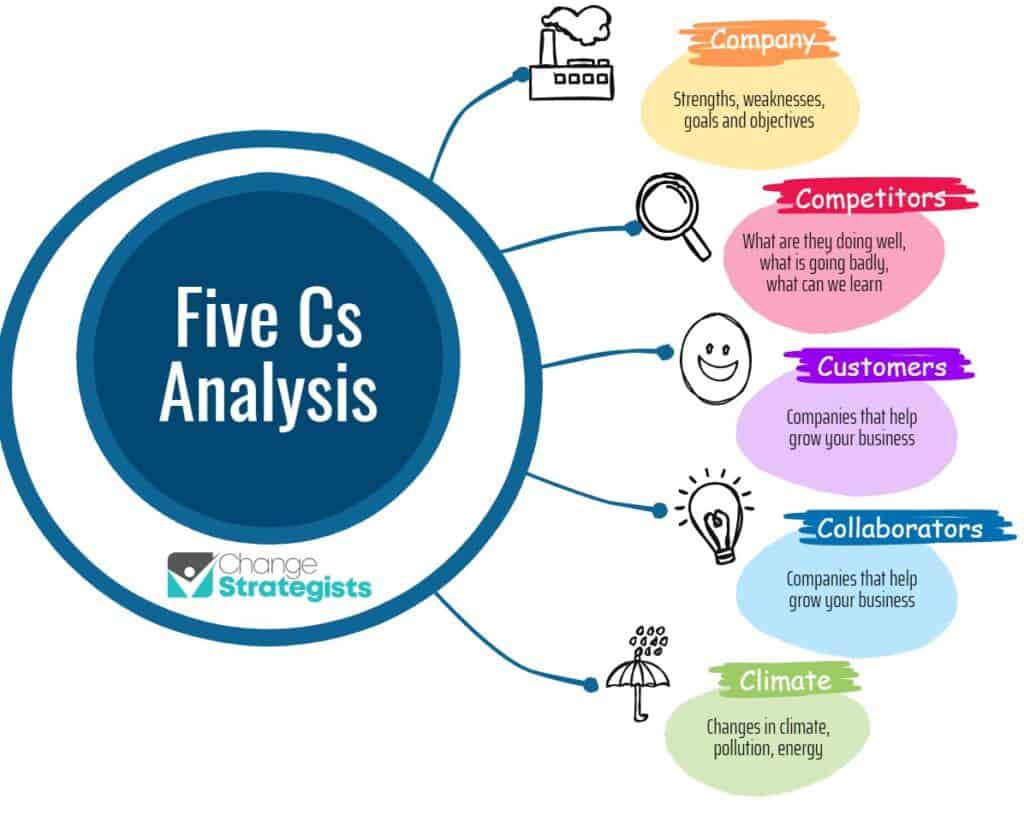
Company
The company analysis considers the enterprise’s goals and objectives, including strengths and weaknesses. It is the most strategic aspect of the analysis.
Competitors
The hallmark of a successful business is surviving the competition and staying ahead. Therefore, understudying your competition is critical for harnessing your business strengths and overcoming your weaknesses.
Customers
More often than not, the customers define the success of a business. Essentially, they are the reason your business exists, and the ultimate goal is always to attract as many customers as possible while retaining precious ones. You need to ensure that your products and services are tailored to meet the needs of your target customers.
Collaborators
As cliche as it sounds, no one is an island, and the same goes for corporate entities. Collaboration is useful in business for driving success. Collaboration is also why business relationships like B2B sales exist, where your company sells its products or services to another company.
Essentially, more businesses make more profit by dealing with other businesses than consumers through partnerships, etc. The reason is that other businesses are more likely to make bulk purchases or orders than direct consumers.
See: Companies That Help Grow Your Business
Climate
Although the climate is easily understood as a place’s weather condition for an extended period. However, it is applicable in business when considering the external factors influencing the business growth rate. The PESTLE analysis we discussed earlier is the perfect concept for how climate affects several firms.
VIRO Analysis
VIRO is an acronym for valuable, imitable, rare, and organized. It is another business analytical tool for evaluating corporate resource management and competition. It allows you to consider whether or not your business is set up for success or failure by ascertaining the value of your products or services.
Is a Business Framework the Same as a Strategic Plan?
A business framework is not the same as a strategic plan, even though both concepts are essential in business management. A plan is a proposal for business achievement, while a framework is a structure behind the plan. You can better understand how they differ through their corporate benefits:
| Business Framework | Strategic Plan |
| Allow more flexibility in adapting to environmental changes. | They are more rigid in adapting to environmental situations because of their precision. |
| They encourage team autonomy due to their broad base. | Team autonomy might be restricted because of its detailed approach. |
| A framework is all inclusive. | Plans can sometimes be exclusive. |
| Frameworks are easier to understand as formulas. | Strategic planning can be cumbersome as a result of the company formula (framework). |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Framework Plan for Companies?
It is a structure for interrelated corporate elements, each having an independent set of values that align with the company’s long-term vision. They include all special features and attributes that contribute to establishing the form and functionality of the business that intertwine with the developmental principles and corporate strategies.
What Is the Purpose of Situational Analysis for Corporate Executives and Consultants?
Corporate executives and business consultants use situational analysis to develop the foundation for analyzing the corporate environment and developing and prioritizing the implementation of action plans.
How Does Situational Analysis Help with the Development of a Company Product?
It provides a framework for identifying the current challenges and opportunities influencing the company’s new product. As a result, the company can quickly advance from its immediate and undesired productivity situation to a more desired situation.
How Can a Situation Framework Benefit Business Consulting?
Business consulting can be more effective by using frameworks in consulting. These frameworks provide a structured approach to analyzing and solving complex business problems. They can help consultants to quickly assess a situation, identify key issues, and offer actionable recommendations for their clients, leading to more efficient and successful consulting engagements.
Final Thoughts
An investigative approach to corporate problems simplifies arriving at effective results. However, with the situation framework, ensuring that the corporate case you are trying to tackle is competitive and strategic to guarantee results is essential. So now that you know when a company should use it, you can enjoy productive business management.





