During the small business phase it’s not uncommon for employees to wear many hats and juggle different projects using nothing more than a notebook. However, in order to really scale a business, there comes a time when it must introduce programme management, but what is programme management?
Programme management is a process which helps an organization adjust their strategy as needed. It takes a high level view of all activities and projects, focusing on the broader outcomes, rather than the specific outputs from individual projects.
Think about how the military works. The top brass have key objectives, and they move units into position, but it’s down to the units to achieve the desired result with the resources allocated to them.
In the business context, the leadership team will set and prioritise desired outcomes. These outcomes could be made up of multiple projects, and it’s the programme managers job to ensure communication is flowing between everyone and that projects stay on track and deliver the desired outcome or outcomes.
Program Management vs. Project Management
A lot of people understand that project management and program management are two important aspects of delivering value to an organization, but they have different focuses.
Project management is the process of leading projects, while program management is more focused around deliverables and larger goals.
Project managers must still manage strategy, but in a more tactical sense. They are concerned with outputs rather than outcomes like their counterparts in program management.
In contrast, program managers need to think about the big picture and how all the individual projects fit into the overall organizational goal.
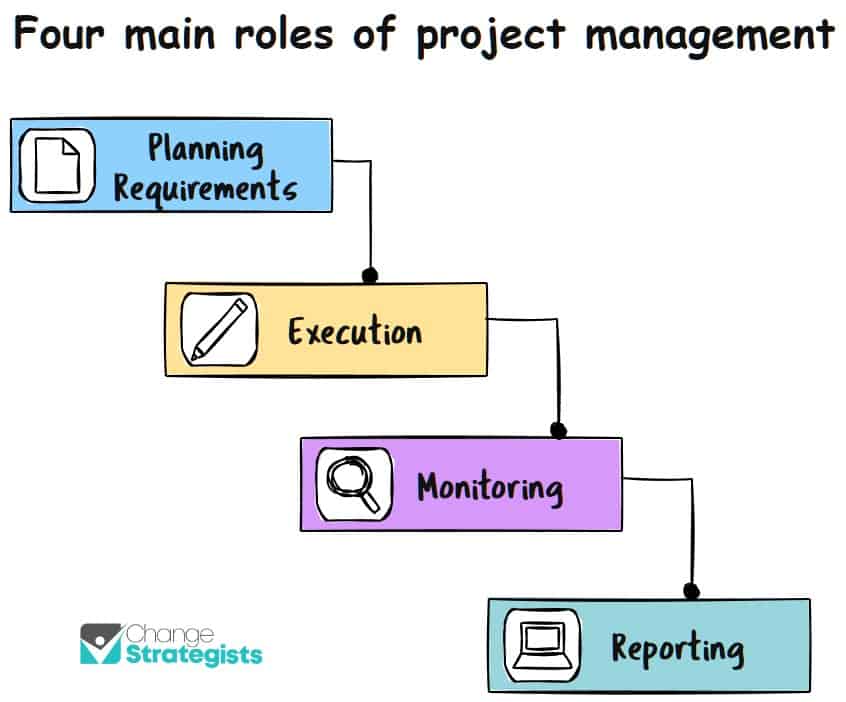
What are the 4 main roles of a project manager?
There are four main roles of a project manager:
Planning: Project managers are responsible for planning the project from start to finish. This includes setting deadlines and milestones, determining scope, and establishing budgets.
Execution: Once the project has been planned, it’s time for the project manager to execute the plan. They do this by assigning tasks to team members, monitoring progress, and ensuring that the project stays on schedule.
Monitoring: As the project progresses, the project manager needs to monitor its progress closely. This means checking in with team members periodically to make sure they’re staying on task, keeping accurate records, and reporting any issues or concerns to the appropriate people.
Reporting: Finally, after the project is complete, the project manager reports back to the sponsor about what happened during the project, whether it met expectations, and if there were any changes needed to improve future projects.
In order to be successful in each of these areas, it’s important for the project manager to have a deep understanding of the project goals and objectives.
There are a lot of overlapping skills required, it’s just that project management involves getting into the fine details about how to create the desired outputs.
What do we mean by outputs and outcomes?
A project is focused on outputs. It has a specific scope that is limited to that particular output, which could involve creating a new product, replacing outdated systems or improving customer satisfaction.
A program is focused on outcomes, e.g. has a new product launched, a new system been introduced or customer satisfaction increased. Programs are fluid and have many unknown deadlines due to their large scope and impact over an extended period of time.
Successful program management can drive long-term business goals or initiatives.
What is the role of program management?
Business programs are an essential part of any organization’s success. They provide the framework for the company’s strategic direction, set goals, and align resources across departments.
So what should you expect a program manager to do in order to manage a business program? What are the key components of a successful program? And how do you ensure that your program delivers results?
Developing and Implementing Programs
A business program manager develops and implements programs within the context of his/her organization. This means that he/she works closely with senior leaders and stakeholders to develop the overall business strategy, plans, and tactics that drive the overall objectives of the organization.

Program managers are responsible for ensuring that the programs they implement are aligned with organizational strategy and deliver measurable outcomes.
They may also be involved in developing and implementing training programs for employees.
Managing Program Resources
A business program manager manages the resources needed to support the implementation of programs. These include human resources, technology, budget, and other necessary tools.
They ensure that these resources are available and accessible to those who need them. He/she also monitors performance against established metrics and makes adjustments where appropriate.
Monitoring and Evaluating Results
A business program manager must monitor and evaluate the results of programs. This involves tracking progress against defined metrics and reporting back to stakeholders.
This requires them to identify areas of improvement and adjust course accordingly.
The ultimate goal of a business program manager is to create value for the organization. To achieve this, he/she needs to understand the organization’s vision, mission, and values.
They should also know the strengths and weaknesses of the organization and its people.
Finally, they need a clear understanding of the market and industry in which the organization operates.
These skills are vital to being a successful business program manager.
What are the three activities that define program management?
Broadly speaking, there are three key activities involved in program management:
- Goal setting: The process of creating and agreeing upon a set of goals for a program.
- Resource allocation: Once the goals have been established, the next step is to allocate resources in order to achieve them. This includes people, money, equipment, and time.
- Risk management: Finally, risk management must be undertaken in order to identify potential risks and develop plans to mitigate them.
This list doesn’t do justice to those in the role, their aim is to ensure all program goals are successful, and all strategic objectives are met, and that often means having to juggle multiple responsibilities at the same time.
What are the key components of programme management?
We’ve taken a look at the key responsibilities, now let’s take a look at the everyday elements of program management.
Managing multiple projects
Program management is a more holistic approach to multiple projects, which are often aligned with strategic goals.
In order to successfully manage these projects, programme management includes a lot of planning and tracking features in order to align projects according to strategic goals.
It can be difficult to do this without the use of software like Asana, which offers great programme management features.
Optimizing resources across projects
Program management should focus on achieving a shared strategic vision by balancing resources with priorities.
Regular communication with the various project managers ensures resources can be correctly allocated and reallocated as priorities change.
Program management helps the organization optimize its resources by taking a more strategic view of project delivery.
By definition, program managers are viewed as strategy execution leaders and have deep knowledge about current organizational capabilities – they can see where improvements can be made and how best to allocate resources in order to achieve success.
The program management process starts with idea to delivery, with continuous planning being a part of every strategic roadmap.
Maximizing benefits across projects
Programme management provides benefits to teams by improving communication, aligning goals and objectives, measuring performance and mitigating risk.
Programs allow the organisation to translate strategy into actionable goals for success, and this requires communicating the business objective and resulting business benefits to those involved.
Program management can be executed at a team level or used as a program that spans across multiple teams within an organisation.
Metrics are aligned with the overall goals of a program and will help define projects and their intended value, which may change as strategy changes.
Monitoring key metrics is important for measuring return on investment and financial success. Examples of different types of result metrics include:
Operational metrics: Has the business measured an improved performance?
Customer satisfaction metrics: Has the business measured increasing customer satisfaction or a reduction in the number of complaints?
Financial metric: Has the business increased revenue? Decreased costs? Or reduced expenses?
Monitoring metrics allows the program manager to understand if the strategic plan has been successful, and if not, to take corrective action as required.
Ensuring successful delivery of projects
A program manager is responsible for the coordination of multiple projects. The focus of a program manager is not just on one project but how these projects are working together to achieve a shared strategic vision.
This requires regular monitoring of projects, stakeholder management, and problem solving keeping the larger goal in mind.
A program manager is viewed as an execution leader who has deep knowledge about current organizational capability.
What are the three activities that define program management?
There are three primary activities that define programme management:
- Developing and managing a portfolio of projects that work together to deliver on the business goals of the organization
- Planning and orchestrating the work across those projects in an efficient way
- Monitoring progress and ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of what is happening and accountable for their part
What are the challenges associated with managing programmes?
When it comes to managing programmes, there are a few challenges that can arise. One of the biggest issues is determining whether the programme is actually delivering benefits.
Without proper measurement and tracking, it can be difficult to ascertain whether objectives are being met.
In addition, most programmes have a lot of moving parts, and it can be difficult to keep track of them all, particularly if different teams are working on different aspects of the same project.
Furthermore, changes in personnel or company priorities can impact a programme’s ability to deliver on its goals.
Finally, communicating effectively with all stakeholders involved in a programme can be challenging, but it’s essential for ensuring that everyone is on the same page and understands what needs to be done in order to achieve success.
What processes are involved in programme management?
There are a few processes that are always involved in programme management. The first is the preparation for steering committee meetings.
This involves getting all the necessary information together and ensuring that everyone who needs to attend is prepared for the meeting. Attendees could be drawn from across the business, from department management to senior positions.
Steering committee meetings should be held at regular intervals, relevant to the time frame of the program. This allows problems to be discussed, ‘course corrections’ to be made, and updates to be shared.
Another key process in programme management is creating and managing work packages. Work packages are essentially groups of tasks that need to be completed in order for the project to be successful.
They help keep everyone on track and ensure that no steps are skipped or duplicated.
Lastly, programme managers also need to track progress throughout the program and report back to stakeholders regularly.
What tools and techniques are used in programme management?
Programme management is a complex process, and as such, programme managers use a variety of tools and techniques to help them manage their programmes effectively. Some of the most common tools used by programme managers include:
Visualizations: Programme managers use visualisations like Gantt charts to see the big picture and track progress on all their projects at a glance. This helps them stay organized and keep everyone on track.
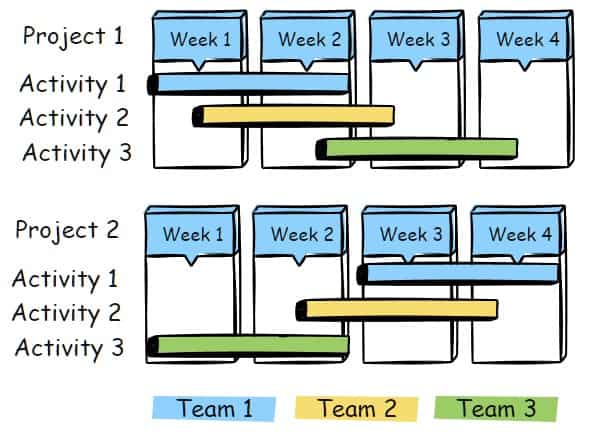
Project Management Tools: Programmes are often more complex than projects, so programme managers need powerful project management tools to help them manage everything. These tools allow them to plan in detail, build out roadmaps, track progress, and more.
Communication Tools: Good communication is essential for successful programmes, so programme managers rely on communication tools like email, chat apps, and video conferencing to keep everyone up to date.
What are the key principles of effective programme management?
There are several key principles of effective programme management. The first is that programme managers need to have practical communication skills, including writing and verbal ones.
Program managers need to be able to set direction for the programme they oversee and have the ability to analyze problems that arise.
They must also provide a clear, concise and comprehensive status update to the relevant audience. This could be key stakeholders, to those involved in a specific project, or to the business at large.
They must be willing to ask questions in order to determine how well projects are doing against expectations and goals, and they must be willing to dive into details of projects when obstacles arise. Unfortunately, this can make them unpopular, especially if senior managers feel someone junior to them is questioning aspects of their work.
Finally, program managers must establish themselves as both senior leaders and day-to-day spokespersons for their executive sponsors.
What are the key stages of a program management lifecycle?
With so much responsibility, you might be wondering how anyone manages to keep on top of it all. It can be very helpful to consider the overall lifecycle of a business program.
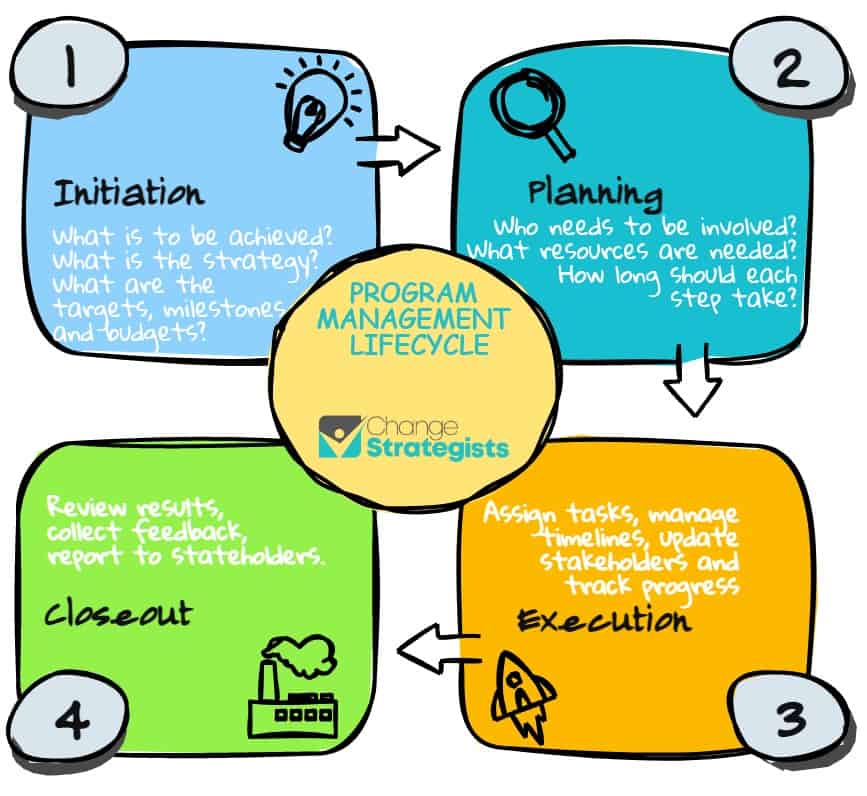
The 4 steps in the programme management lifecycle are:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Closeout
Initiation: In this stage of the programme management lifecycle, programme managers start with an idea about what they want to achieve. They then develop a strategy for achieving these objectives, which may involve setting targets, creating milestones, and establishing budgets.
Planning: In this stage of the lifecycle, programme managers will develop a detailed plan for the programme. They’ll identify who needs to be involved, what resources will be needed, and how long each step should take.
Execution: Once the plan has been developed, programme managers will execute the plan by assigning tasks, managing timelines, and tracking progress.
Closeout: Finally, once the programme is complete, programme managers will close out the programme by reviewing results, reporting back to stakeholders.
The project itself may have elements that continue, especially when it comes to quality assurance, where teams work to ensure that all deliverables meet expectations for quality. This often involves rigorous testing procedures to identify any potential issues before they can cause problems down the line and while it is often done during the project, it can continue for some time afterwards a part of the business as usual process.
How can programme management be used to achieve organisational objectives?
If you’ve made it this far I hope you’ve gained a good understanding of this role. To recap:
Programme management can be used to achieve organisational objectives by developing and managing multiple projects at once. In doing so, programme managers are able to increase efficiency and productivity in the workplace.
Additionally, programme managers are able to facilitate communication between cross-functional teams, which can lead to better collaboration and increased productivity.
Finally, as a business grows in size, the use of a single point of contact for all strategic activities will help the business scale and ensure that all projects remain on track.
What are the benefits of using programme management methodology?
Let’s recap the key benefits of this approach:
- The first and most obvious benefit is that it allows for cross-functionality and the execution of strategy across different teams in an organization.
- It allow organizations to measure performance and mitigate risk. This is done through the use of goal-setting which can be tailored to specific programs.
- This methodology provides a means of measuring the success of the program. It’s important to align metrics with strategic goals, not just side projects; this will help ensure that programs are actually contributing value back to the company.
- Using this approach helps organizations be more flexible as they change along their way; changes are inevitable, but with good planning they can be accommodated without too much disruption.
- Monitoring metrics (e.g. financial metrics, operational metrics, customer experience metrics etc.) provides a well-rounded view of how the program, and business, is performing overall.
- This methodology is useful for managing projects that have multiple stages and varying time frames, which is often the case with larger programmes spanning multiple years or even decades!
- This methodology helps proactively identify potential risks and put measures in place to reduce their impact on organizational performance.
- It helps stakeholders communicate more clearly and accurately, not only with one another, but with the business. This improved communication results in better understanding and faster resolution of issues.
- Finally, good programme management practices leads to the setting up of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) which can be used to track the progress of a project or the programme as a whole.
In short, there are many benefits to using a Programme Management methodology in order to successfully manage projects!
What are the key success factors for effective programme management?
With so much day to day management taking place it’s easy to lose sight of the key elements to achieving the program goals. Of all the factors, this is one of the most critical:
Communication is a key factor for the success of any program or project management. The manager needs to be able to communicate effectively with all stakeholders, from team members to senior executives.
Everything else flows from this skill: you need to set directions, collect feedback, provide reports and status updates, all of this requires good communication skills.
Of course, problem-solving skills are also key for any successful program manager; when things go wrong, they need to be able to quickly find a solution so that the project can continue moving forward.