The PCT Model is a tool for managing change in organizations. It stands for Prosci Change Triangle and helps you see what’s needed for successful change. The PCT Model shows four key parts of change: success, leadership, project management, and change management.
You can use this model to check how healthy your change project is. It helps you spot problems and fix them early. The PCT Model is easy to understand and use, even if you’re new to change management.
By using the PCT Model, you can make your change projects more likely to succeed. It helps you focus on what’s important and make sure all parts of the change are working well together. This can save you time and money in the long run.
Overview of the Prosci Change Triangle (PCT) Model
The Prosci Change Triangle Model helps you understand and improve key aspects of project success. It shows four critical elements that work together for effective change.
History and Evolution
The PCT Model was first introduced in July 2006. Prosci created it to help change management professionals and project teams. Since then, it has become a widely used tool.
The model has grown more popular over time. Many organizations now use it to plan and carry out changes. It’s part of Prosci’s larger change management approach.
As change management has evolved, so has the PCT Model. It now fits with other Prosci tools and methods. This makes it even more useful for managing change.
Fundamental Principles
The PCT Model is based on some key ideas:
- Change needs four main things to work well.
- These four parts are linked and affect each other.
- If one part is weak, the whole change can struggle.
The model starts with success in mind. This means you think about what a good result looks like from the start.
You can use the PCT Model to:
- Check how healthy your project is
- Find areas that need work
- Make your change efforts stronger
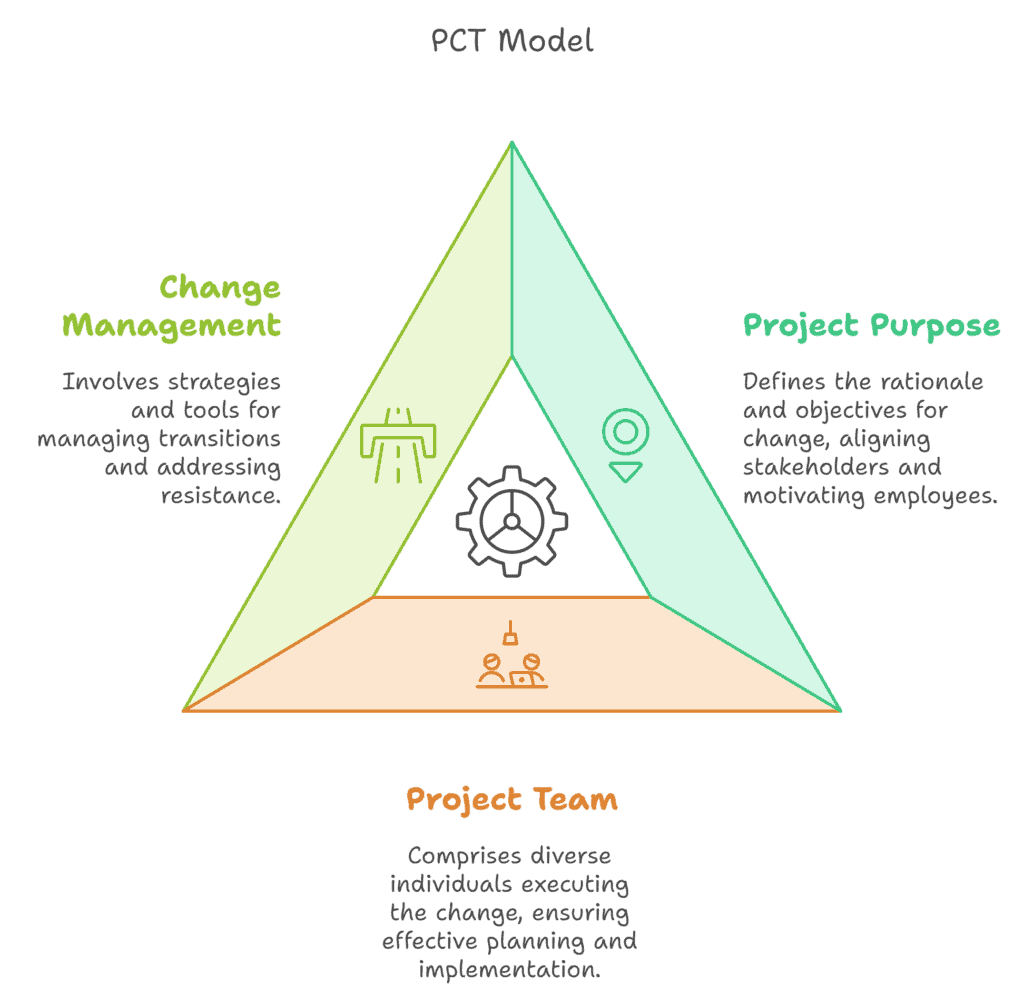
Components of the PCT Model
The PCT Model has four main parts:
- Success: What you want to achieve
- Leadership/Sponsorship: Support from top leaders
- Project Management: How you plan and run the project
- Change Management: How you help people adapt
These parts form a triangle shape. Success is at the top. The other three make up the sides.
Each part is important. If one is weak, your project might have trouble. For example, without good leadership, even a well-planned project can fail.
You can use the PCT Model to look at each part closely. This helps you see where you’re doing well and where you need to improve.
Leadership and Sponsorship
Leadership and sponsorship are key to successful change efforts. They provide direction, support, and resources needed for change initiatives to succeed.
Role of Leadership in Change Management
Leaders play a crucial part in guiding change. You need strong leadership to set the vision and strategy for change. Leaders make important decisions about change projects. They allocate resources and remove obstacles.
Effective leaders communicate the reasons for change. They help employees understand why change is necessary. You’ll find that good leaders model the desired behaviors. They show commitment to the change through their actions.
Leaders also build coalitions to support change efforts. They engage key stakeholders and address concerns. Your leaders should inspire and motivate others during the change process.
The Importance of Effective Sponsorship
Sponsorship is vital for change success. As a sponsor, you actively and visibly support the change initiative. You use your influence to gain buy-in from others in the organization.
Effective sponsors provide resources and remove barriers. You make sure the change team has what it needs to succeed. Sponsors also help manage resistance to change.
Good sponsorship increases the likelihood of change adoption. You’ll see better results when sponsors stay engaged throughout the process. They reinforce the change message and celebrate successes.
ABC’s of Sponsorship
The ABC’s of Sponsorship are a helpful guide for business leaders. They stand for Active and visible participation, Building a coalition, and Communicating directly.
Active participation means you’re visibly involved in the change. You attend key events and show your support. Building a coalition involves getting other leaders on board. You create a network of sponsors at different levels.
Direct communication is crucial. You share messages about the change with employees. Be clear about expectations and the reasons for change. Use various channels to reach your audience.
These ABC’s help you fulfill your sponsorship role effectively. They ensure you’re providing the right level of support for change initiatives.
Defining Success in Change Initiatives
Success in change initiatives involves clear goals, measurable outcomes, and widespread adoption. It requires balancing project objectives with organizational benefits and tracking progress through key metrics.
Project Objectives and Health
Project objectives form the backbone of any change initiative. You need to set clear, specific goals that align with your organization’s vision. These objectives should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Project health is crucial for success. You must regularly assess progress and address any issues promptly. This includes monitoring:
- Timeline adherence
- Budget management
- Resource allocation
- Risk mitigation
By keeping a close eye on these factors, you can ensure your project stays on track and delivers the intended results.
Organizational Benefits and Adoption
Organizational benefits are the positive outcomes your change initiative brings. These may include:
- Increased efficiency
- Cost savings
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Enhanced employee engagement
To maximize these benefits, you need to focus on adoption. This means getting your team to embrace and use the new processes or systems.
Strategies to boost adoption:
- Clear communication of benefits
- Adequate training and support
- Recognition of early adopters
- Addressing resistance promptly
Measurements of Success
To gauge the effectiveness of your change initiative, you need concrete measurements. These metrics help you track progress and demonstrate value to stakeholders.
Key success measurements may include:
- Adoption rate
- Productivity improvements
- Cost reductions
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Employee feedback
You should establish baseline metrics before the change and regularly measure progress. This allows you to make data-driven decisions and adjust your approach if needed.
Remember to celebrate small wins along the way. This helps maintain momentum and keeps your team motivated throughout the change process.
Assessing Project and Change Effort

The PCT Model helps evaluate and improve change initiatives. It focuses on key areas that determine project success and provides tools for effective management.
PCT Assessment and Its Usage
The PCT Assessment is a valuable tool for measuring project health. You can use it to evaluate four critical aspects: success, leadership, project management, and change management.
This assessment helps you identify strengths and weaknesses in your change effort. You’ll get a clear picture of where improvements are needed.
Use the PCT Assessment at different stages of your project. It’s helpful at the start, during execution, and near completion. This allows you to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
The results provide insights into team alignment and resource allocation. You can use this information to make data-driven decisions about your change initiative.
Identifying and Managing Risks
Risk identification is crucial for project success. The PCT Model helps you spot potential issues early on.
Look for gaps in leadership support, project management, or change management. These are common risk areas in change efforts.
Pay attention to stakeholder resistance. It’s a major risk factor in many projects. Use the PCT Assessment to gauge stakeholder buy-in and engagement.
Develop strategies to address identified risks. This might involve additional training, communication plans, or resource reallocation.
Monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle. Regular assessments help you stay ahead of potential problems.
Create contingency plans for high-impact risks. This preparation can save time and resources if issues arise.
Action Plans for Successful Implementation
Based on your PCT Assessment results, create targeted action plans. These should address specific areas needing improvement.
Focus on quick wins to build momentum. Identify actions that can show immediate positive results.
Involve key stakeholders in plan development. Their input increases buy-in and improves plan effectiveness.
Set clear, measurable goals for each action item. This helps track progress and demonstrate success.
Assign responsibilities and deadlines for each action. Clear ownership ensures accountability.
Review and update action plans regularly. As your project evolves, so should your strategies.
Consider using SMART goals when crafting your action items. This approach helps create focused, achievable plans.
Change Management Strategy and Execution

The PCT model links change management strategy to project success. It focuses on key elements like integration, teamwork, and employee engagement.
Integrated Approach to Project and Change Management
Project management and change management work together in the PCT model. You’ll find they support each other to reach project goals. This team effort helps reduce resistance to change.
Project managers handle tasks and timelines. Change managers focus on people’s needs. When they join forces, you get better results.
This approach boosts your chances of success. It makes sure technical and people sides of change align. You’ll see smoother transitions and fewer setbacks.
Coalition of Support and Change Teams
Building a strong coalition of support is vital. You need backing from leaders and key players. This group champions the change across your organization.
Your change team works closely with this coalition. They plan and carry out change activities. The team includes people from different parts of your company.
Together, they create a powerful force for change. They address concerns and build excitement. This united front helps push through barriers to change.
Engagement and the ADKAR Model
Employee engagement is key to successful change. The ADKAR model guides this process. It stands for Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement.
You use ADKAR to help people through change stages. First, make them aware of why change is needed. Then, build their desire to take part in the change.
Give them knowledge about how to change. Help them gain the ability to implement new skills. Finally, reinforce the change to make it stick.
This step-by-step approach keeps people engaged. It turns resistance into support. You’ll see better adoption of new ways of working.
Aligning Project Management with Change Management
Integrating project management and change management creates a powerful approach for successful organizational changes. This alignment ensures both technical and people-side aspects are addressed throughout the project lifecycle.
Project Management Approach and Considerations
When aligning project management with change management, you need to consider how both disciplines interact. Project management and change management share common goals, like delivering successful outcomes and realizing benefits.
Key considerations include:
- Scope: Define project boundaries and change impacts
- Schedule: Align technical milestones with people-side activities
- Resources: Allocate time and budget for change management efforts
- Risks: Identify and mitigate both technical and people-related risks
By integrating these elements, you create a more comprehensive project plan that addresses both the technical and human aspects of change.
Evaluating Project Health in Conjunction with Change Management
To assess project health, you should look beyond traditional metrics and include change management factors. The Prosci Change Triangle (PCT) Model provides a framework for this integrated evaluation.
Key areas to evaluate:
- Technical side: Project progress, milestones, deliverables
- People side: Readiness, adoption, usage
- Organizational alignment: Leadership support, resources, funding
Regular assessments help you identify potential issues early and make necessary adjustments. This holistic approach ensures your project stays on track from both technical and people perspectives.
The Role of Project Managers and Change Practitioners
Project managers and change practitioners play crucial roles in aligning project and change management efforts. Their collaboration is key to project success.
Project managers focus on:
- Delivering technical solutions
- Managing timelines and resources
- Coordinating project teams
Change practitioners concentrate on:
- Preparing people for change
- Designing adoption strategies
- Supporting user transition
By working together, these professionals create a more integrated approach that addresses both technical and people-side challenges. This collaboration helps ensure your project delivers its intended benefits and achieves lasting organizational change.
Learning and Development
The PCT model provides valuable learning opportunities for change professionals. Training programs and educational resources help build key skills for implementing successful organizational changes.
Training for Change Practitioners and Project Managers
Change practitioners and project managers can benefit from specialized PCT model training. You’ll learn how to apply the model’s four aspects to real-world projects. Courses cover defining success criteria, securing leadership support, and integrating change management with project management.
Hands-on workshops let you practice using PCT assessment tools. You’ll analyze case studies and develop action plans to address gaps. Role-playing exercises help build sponsorship and stakeholder engagement skills.
Certification programs are available to demonstrate your PCT model expertise. These typically involve coursework, exams, and practical application of the model on actual projects.
Educational Resources and Webinars
Webinars offer flexible learning options for busy professionals. You can join live sessions or watch recordings on PCT model topics. Expert presenters share tips and answer questions in real-time.
Free resources like whitepapers and articles provide in-depth explanations of PCT concepts. You’ll find practical guides for using the model in different industries and project types.
Online forums let you connect with other practitioners to share experiences. Video tutorials demonstrate how to use PCT assessment tools and interpret results.
Self-paced e-learning modules allow you to study key PCT principles on your own schedule. Interactive quizzes help reinforce your understanding of the model’s components.




