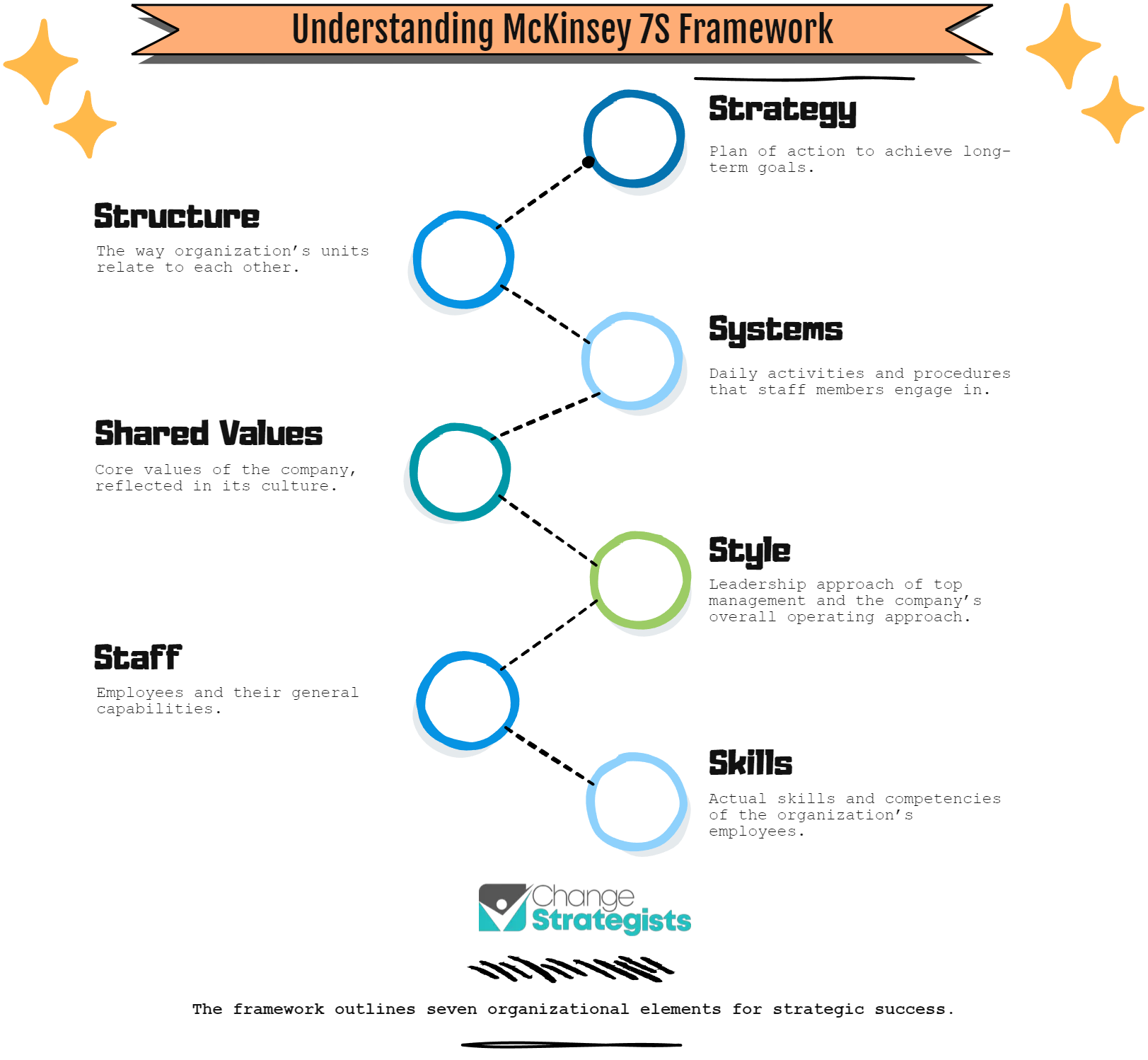
The McKinsey 7S Framework is a comprehensive tool for analyzing and improving organizational effectiveness.
Developed in the late 1970s by McKinsey & Company consultants, it provides a framework for examining the complex interrelationships within an organization.
This model focuses on seven key internal elements that need to be aligned for a company to reach its strategic objectives and perform effectively.
Understanding how to use the McKinsey 7S Framework is crucial for leaders and managers seeking to implement changes or to better align their organizations with their strategic visions.
Applying the 7S Model involves evaluating and aligning the seven elements, which are categorized as either ‘hard’ or ‘soft’. The ‘hard’ elements refer to strategy, structure, and systems, which are often quantifiable and can be directly influenced by management.
On the other hand, the ‘soft’ elements, which consist of shared values, skills, style, and staff, are more rooted in the company’s culture and are less tangible, yet they have a significant impact on an organization’s success.
Balancing these elements helps to diagnose problems, guide organizational change, and enhance overall performance.
Key Takeaways
- The McKinsey 7S Framework is integral to strategic planning and organizational effectiveness.
- It consists of seven interrelated elements divided into ‘hard’ and ‘soft’ categories.
- Proper application ensures alignment of the elements to achieve business objectives.
Understanding the McKinsey 7S Framework
The McKinsey 7S Framework is an organizational model that analyzes seven distinct aspects of a business for alignment and integration. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of the elements that determine organizational effectiveness.
Overview of the Hard and Soft Elements
Hard Elements:
- Structure: The architecture of an organization, detailing the hierarchy and network of relationships.
- Strategy: The plan devised to maintain and build competitive advantage.
- Systems: The procedures and processes that underpin day-to-day activities.
Soft Elements:
- Skills: The capabilities and competencies of the company’s employees.
- Staff: The human resources and how they are managed and developed.
- Style: The characteristic way in which the organization and its leaders communicate and behave.
- Shared Values: Formerly called “Superordinate Goals,” these are the core values that are deeply ingrained in the company’s culture and serve as a guiding compass.
Origins and Evolution of the Framework
Introduced in the late 1970s by McKinsey consultants Tom Peters and Robert Waterman, the McKinsey 7S Framework was a response to the simplification of corporate strategy concepts that were prevalent at the time.
Its development coincided with research for their book, “In Search of Excellence,” and was designed to be a comprehensive tool to diagnose and organize a company’s effectiveness and ability to change. Since its inception, the framework has evolved to recognize the dynamic and complex nature of organizations, underpinning its enduring relevance in the strategic planning space.
Assessing the Seven S Elements
To effectively implement the McKinsey 7S Framework, it’s critical to thoroughly evaluate each of the seven elements to understand their current state and the impact they have on the organization’s ability to reach its objectives.
Strategy Analysis
An organization’s strategy is its plan for outstripping competitors and achieving market leadership. Analysis involves examining the clarity and coherence of strategic goals, how well they respond to market dynamics, and their alignment with internal capabilities.
Structure Review
The structure of an organization determines how tasks and responsibilities are allocated. In reviewing structure, one should analyze the hierarchy, the distribution of authority, and the efficiency of communication channels to ensure they support the organization’s goals.
Systems Evaluation
Systems are the procedures and routines that underpin daily operations. Evaluating these requires a look at information and management systems to ascertain if they are robust enough to support current and future strategies.
Shared Values Assessment
Central beliefs and attitudes, known as shared values, direct employee behavior. This assessment focuses on these core values and how deeply they are embedded within the organization’s culture.
Skills Analysis
Here, one assesses the skills available within the organization and whether they align with strategic demands. This involves not only evaluating the abilities employees possess but also identifying skill gaps that need to be filled.
Style Examination
The style refers to leadership approach and general work culture. Examination of style involves observing leadership behaviors and their effect on the organization’s tone and how decisions are made and executed.
Staff Analysis
Finally, analyzing staff looks at human resources in terms of numbers, competencies, and potential. This analysis explores whether the organization has the right people to meet strategic targets and adapt to changes in the market.
Applying the 7S Model
The McKinsey 7S Framework serves as a comprehensive guide for organizations seeking to enhance performance by aligning key elements. Through structured analysis and implementation, companies can develop strategies that adapt to change while maintaining coherency throughout their structures.
Strategic Planning and Alignment
Strategic planning within the 7S framework requires ensuring that the company’s strategy, structure, and systems are fully aligned. It involves assessing whether the current strategy is apt to meet organizational goals. They must formulate a clear action plan that is attuned to both internal capabilities and external opportunities.
Managing Organizational Change
When managing organizational change, leadership must evaluate and adjust the seven S elements to maintain equilibrium. Adapting management styles and organizational structure may be crucial as changes in one element often necessitate changes in others to sustain alignment.
Achieving and Sustaining Alignment
Achieving and sustaining alignment demands continuous monitoring and recalibration of the 7S components. Management is tasked with ensuring systems, shared values, and staff roles all coalesce to support the implementation of business strategies effectively.
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Effective decision-making and problem-solving hinge on the interconnectedness of the model’s elements. Leaders should use the 7S framework to identify areas where decisions can improve alignment and performance, thereby transforming challenges into actionable solutions.
Organizational Design and Effectiveness
The McKinsey 7S Framework provides a comprehensive approach to organizational design, focusing on aligning key elements for enhanced effectiveness. This section delves into the roles of organizational hierarchy, workflow, and human resources as cornerstones for productivity and talent management.
Examining Organizational Hierarchy
Organizational structure and hierarchy are vital for clarifying roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines within an organization. A well-defined hierarchy streamlines decision-making processes and establishes a clear ladder for escalation and accountability. For example, flat structures may lead to quicker decision times and increased empowerment among staff, while tall structures often feature well-defined, procedural channels for decision-making.
Designing Effective Workflow
Workflow design is instrumental for organizational productivity. Effective workflows incorporate systematic processes where tasks are transitioned smoothly from one stage to the next. This sequence should reflect the organization’s strategy and objectives, ensuring that each department’s activities contribute to the broader goals. Workflow optimization often entails eliminating redundant steps and implementing systems that support efficient resource allocation.
Leveraging Human Resources
An organization’s success is heavily reliant on how well it manages and utilizes its human resources. Talent management involves not only hiring skilled employees but also ensuring they have a conducive environment to thrive in. This requires aligning staff expertise with the company’s strategic needs, fostering professional development, and maintaining morale through recognition and rewards. Effective human resources strategies ensure that the organization’s goals are seamlessly supported by its most valuable assets—its people.
Enhancing Performance and Competitive Advantage
To effectively enhance performance and secure a competitive advantage, organizations must align core values and capabilities with strategic goals. This alignment involves a rigorous analysis of internal and external factors that influence success.
Identifying and Leveraging Capabilities
Organizations must first identify their unique capabilities that drive performance. These include specific skills, staff competencies, and internal processes that provide a distinct advantage in the marketplace. Once identified, leveraging these capabilities means integrating them with the company’s strategy and shared values, ensuring that every aspect of the organization is working towards common objectives.
Benchmarking and Opportunities
Benchmarking is a critical step for organizations to measure performance against the industry best. This provides insights into where a company stands in relation to its competitors and highlights opportunities for improvement. Identifying gaps in the current model can direct focus towards areas with the most potential for growth, allowing organizations to prioritize resources effectively.
Adapting to the External Environment
The external environment is constantly changing, presenting both challenges and opportunities. Adapting to these changes requires a flexible structure and responsive systems. It’s essential for an organization to remain vigilant, monitoring the external environment for shifts in customer preferences, market trends, and regulatory landscapes. Adjusting strategies and operations in response enables an organization to maintain its competitive advantage over time.
Analyzing and Addressing Challenges

When utilizing the McKinsey 7S Framework, businesses must carefully identify and anticipate operational challenges. They should analyze existing weaknesses and inconsistencies to align all elements of the organization effectively, especially during times of restructuring, mergers, or acquisitions.
Conducting Thorough SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis serves as a foundation for identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats within an organization. This analysis should include:
- Strengths: Recognizing organizational capabilities and resources that can be leveraged.
- Weaknesses: Identifying current gaps or areas of underperformance.
- Opportunities: Highlighting potential areas for strategic growth or improvement.
- Threats: Acknowledging external factors that may disrupt operations or stability.
Addressing these components allows businesses to construct a comprehensive overview conducive to strategic planning and management decisions.
Addressing Misalignments and Inconsistencies
The McKinsey 7S Framework emphasizes the importance of alignment between seven key internal factors: strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff. When misalignments occur, they approach resolution by:
- Strategy: Ensuring the organization’s strategy is clear and well-communicated.
- Structure: Adjusting the organizational structure to remove silos and facilitate communication.
- Systems: Overhauling outdated processes or implementing new systems to improve efficiency.
- Shared Values: Realigning the core values to reflect and support the strategy.
- Skills: Identifying skill gaps and investing in training or hiring.
- Style: Modifying the management style to reflect a more suitable approach for the organization’s goals.
- Staff: Aligning staff roles and responsibilities with the organization’s strategic objectives.
By addressing these areas, an organization can improve its overall effectiveness and better navigate the complexities of a merger, acquisition, or restructuring.
Measuring and Improving Organizational Effectiveness

The McKinsey 7S Framework provides a comprehensive approach to assess and enhance organizational effectiveness. It ensures that key internal elements are synchronized for optimal performance.
Utilizing Performance Standards and Metrics
The identification and application of performance standards and metrics are integral for evaluating the current state of an organization. These standards should be clearly defined, quantifiable, and aligned with the company’s strategic goals. Important metrics often include indicators related to productivity, efficiency, and quality of standard operations. Organizations may track metrics such as employee turnover rate, customer satisfaction scores, and operational efficiency rates to gain insights into their performance. This allows leaders to identify areas that require attention and improvement.
Communication throughout the workforce about these performance standards ensures that everyone is aware of expectations and can work in unison towards common organizational goals. Metrics should not only be used as a gauge but also as a means to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Investing in Training and Development
Investing in the training and development of the workforce is crucial for maintaining and enhancing organizational effectiveness. By focusing on building the skills and capabilities of employees, an organization can ensure its operations remain competitive and innovative. The McKinsey 7S Framework emphasizes aligning skills with business needs, which often involves:
- Formal Training Programs: To systematically elevate the knowledge base of employees.
- On-the-Job Development: Practical experience that complements theoretical knowledge.
- Mentoring and Coaching: One-to-one support to advance personal and professional growth.
Additionally, effective communication about training programs and opportunities encourages employee engagement and conveys the value placed on personnel development. A workforce that is well-trained and up-to-date with industry standards is better equipped to adapt to changes and contribute to the organization’s success.
Case Studies and Practical Applications
Through concrete case studies and real-world applications, one can discern the tangible benefits and potential drawbacks of utilizing the McKinsey 7S Framework in various industries. These examples illuminate how consultants have applied the framework to assess and enhance organizational effectiveness, highlighting the strategic value of alignment across the seven internal elements in making substantial organizational changes.
Real-World Examples from Industry
Numerous organizations across different industries have applied the McKinsey 7S Framework to facilitate effective transformations. In one case, a leading manufacturing company used the model to integrate a newly acquired subsidiary. Consultants focused on aligning the Shared Values and Styles of both entities to ensure a smooth transition. This synergy facilitated a unified approach to setting up the Systems and Structures that would govern the new joint operations.
Another example involved a financial services firm that faced operational inefficiencies due to outdated technology. The application of the McKinsey 7S Model helped in identifying inconsistencies between their Strategy, existing Systems, and the Skills necessary to drive innovation. This resulted in a targeted staff training program and upgrading of systems, which restored the firm’s competitive edge.
Lessons Learned from Successful Implementations
The McKinsey 7S Framework has been a preferred approach by consultants aiming to implement holistic changes in an organization. From successful projects, it’s clear that one advantage offered by the framework’s holistic approach is the ability to identify and reinforce strong links between an organization’s structure and strategy, ensuring a thorough and cohesive transformation.
However, case studies also emphasize the framework’s disadvantage, which can be its complexity and the time consumption in addressing all seven elements effectively. For instance, a telecommunications company might still struggle with adapting its Style and Skills post-strategy revamp, which underlines the need for ongoing adjustments and perhaps even a phased approach to implementation.
Implementing changes in an organization can be complex, but through analyzing these case studies, it is evident that the McKinsey 7S Framework can serve as a comprehensive guide for consultants and companies alike to navigate these complexities with confidence and clarity.
Conclusion
The McKinsey 7S Framework remains a valuable tool for organizational analysis and integrated change management. By scrutinizing the seven elements—Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff—organizations can gain a comprehensive view of their current operational state and pinpoint areas for improvement.
One should approach the framework with a view that these elements are interconnected; thus, a change in one will likely impact the others. It is crucial for an organization to maintain a balance between these elements to ensure effective implementation of strategies and operational efficacy.
When utilizing the McKinsey 7S Framework, an organization must:
- Conduct an honest assessment of each element
- Identify areas where change is needed
- Develop a plan for alignment and transformation
- Ensure that the changes contribute to a cohesive organizational culture and vision
Regular reevaluation using the framework can help organizations stay aligned with their strategic vision and adapt to internal or external changes. This disciplined approach to analysis and change can position organizations to navigate complex challenges and enhance their long-term success.
In summary, leaders and managers should integrate the McKinsey 7S Framework into their strategic planning and organizational development efforts to build a resilient and adaptive enterprise.
Frequently Asked Questions
The McKinsey 7S Framework is a valuable tool for assessing and aligning organizational elements to optimize performance. These questions commonly arise when leaders and managers look to apply the framework within their strategic management processes.
What is the McKinsey 7S Framework and how is it applied in strategic management?
The McKinsey 7S Framework is a comprehensive model used to analyze and improve a company’s organizational effectiveness. By examining seven internal components—strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff—leaders can ensure they are harmoniously aligned to the organizational goals, thus facilitating successful strategic management implementation.
Can you provide an example of how a company has successfully applied the McKinsey 7S Framework?
A company, such as Starbucks, has successfully utilized the McKinsey 7S Framework to maintain alignment between their growth strategies and operating procedures, especially when expanding globally. They do this by continuously reassessing and realigning these seven elements to sustain their market position and corporate culture.
What are the hard and soft elements of the McKinsey 7S Framework, and why are they important?
The hard elements include strategy, structure, and systems which are tangible and easier to identify. The soft elements—shared values, skills, style, and staff—are less tangible but crucial because they represent the human factors in the organization. Both sets are critical because they represent all facets necessary for organizational success and must be aligned for effective execution.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of utilizing the McKinsey 7S Model in organizational analysis?
Advantages of the McKinsey 7S Model include its holistic view of the organization and the interconnectedness it promotes between various elements. However, disadvantages may arise from its inherently qualitative approach, making it less prescriptive and potentially subject to bias in interpretation and analysis.
How is the McKinsey 7S Framework beneficial for implementing effective change within an organization?
The McKinsey 7S Framework assists in highlighting areas of misalignment and provides a guideline for enacting changes across the organization’s core aspects. Effective change often requires considering all seven elements to ensure that they support and reinforce each other, leading to successful implementation and adoption.
What steps should be taken to effectively apply the McKinsey 7S Framework when formulating a new strategy?
When formulating a new strategy using the McKinsey 7S Framework, it is recommended to start by identifying current alignments and inconsistencies across the seven elements. This is followed by iterative adjustments to each component, ensuring they are in sync with the new strategy, culminating in a comprehensive approach to strategy execution.