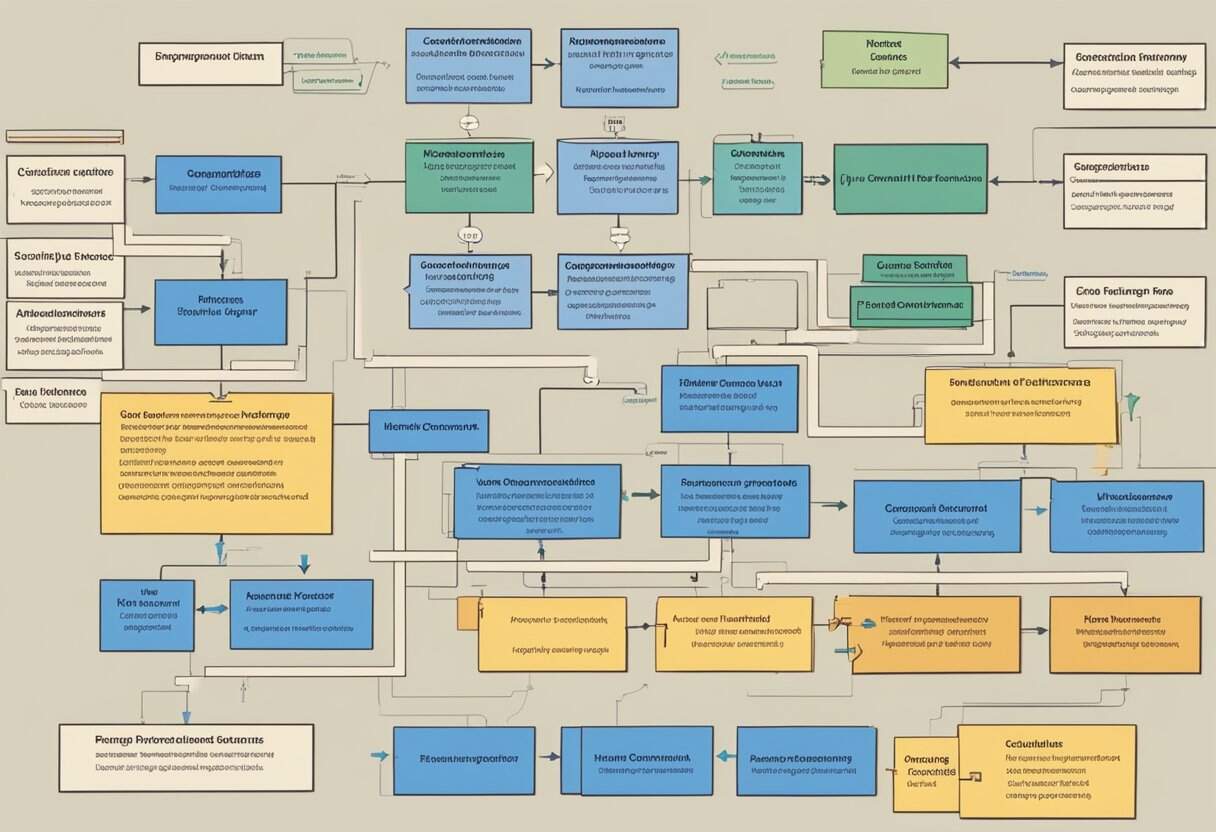
The Burke-Litwin Model is a powerful tool for understanding and managing change in organizations. It helps you see how different parts of a company work together and affect each other during times of change. The model identifies 12 key factors that influence organizational performance and shows how they are connected.
You can use this model to figure out what needs to change in your company and why. It looks at things like the outside environment, company goals, leadership, and company culture. By using the Burke-Litwin Model, you can make better plans for change and see how one change might affect other areas of your business.
This model is useful for managers, leaders, and anyone involved in making changes at work. It can help you understand the drivers of change and make smart choices about how to move your organization forward. Whether you’re dealing with small updates or big transformations, the Burke-Litwin Model can guide your efforts and improve your chances of success.
Overview of the Burke-Litwin Model
The Burke-Litwin Model is a framework for understanding organizational change. It was developed by George H. Litwin and W. Warner Burke in the 1960s. This model helps you analyze how different parts of an organization affect each other during change.
The model includes 12 key elements that influence organizational performance. These elements are divided into two main categories:
Transformational Factors:
- External Environment
- Mission and Strategy
- Leadership
- Organizational Culture
Transactional Factors:
- Structure
- Management Practices
- Systems
- Work Unit Climate
- Task Requirements and Individual Skills
- Individual Needs and Values
- Motivation
- Individual and Organizational Performance
The Burke-Litwin Model is based on open systems theory. This means it considers how external factors can impact internal organizational dynamics.
When you use this model, you can identify which areas of your organization need attention during change initiatives. It helps you understand the relationships between different organizational elements and their impact on performance.
By applying the Burke-Litwin Model, you can create more effective change strategies. It allows you to focus on the most important factors driving change in your organization.
Transformational Factors
The Burke-Litwin Model highlights key factors that drive significant organizational change. These factors have a deep impact on an organization’s identity and ability to adapt to new challenges.
External Environment
The external environment plays a crucial role in shaping organizational change. It includes factors outside your control that affect your business. These can be:
- Economic conditions
- Market trends
- Technological advancements
- Regulatory changes
You need to constantly monitor these external factors to stay competitive. When the environment shifts, your organization must adapt quickly. This might mean changing your products, services, or even your entire business model.
For example, if new technology emerges in your industry, you may need to invest in it to keep up with competitors. Or if consumer preferences change, you might need to adjust your offerings to meet new demands.
Mission and Strategy
Your organization’s mission and strategy are the foundation for all other transformational factors. They define why your company exists and how it plans to achieve its goals.
A clear mission statement guides decision-making at all levels. It helps you:
- Focus on what’s important
- Align resources effectively
- Motivate employees
Your strategy outlines the specific steps you’ll take to fulfill your mission. It should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the external environment while staying true to your core purpose.
Regular strategic planning sessions can help you review and adjust your mission and strategy as needed. This ensures your organization remains relevant and competitive in a changing landscape.
Leadership
Strong leadership is essential for driving transformational change. Leaders set the tone for the entire organization and play a key role in:
- Communicating the vision
- Inspiring and motivating employees
- Making critical decisions
Effective leaders in the Burke-Litwin Model are:
- Visionary – They see the big picture and plan for the future
- Adaptable – They can adjust their approach as circumstances change
- Communicative – They keep everyone informed and aligned
You need leaders who can guide your organization through periods of uncertainty and change. They should be able to balance short-term needs with long-term goals.
Organizational Culture
Your organizational culture is the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that shape how work gets done. It’s a powerful force that can either support or hinder change efforts.
A culture that embraces change is:
- Open to new ideas
- Willing to take calculated risks
- Focused on continuous learning and improvement
To create a change-friendly culture, you can:
- Encourage innovation and experimentation
- Celebrate successes and learn from failures
- Promote open communication at all levels
Remember, culture change takes time. It requires consistent effort and reinforcement from leaders and employees alike. But a strong, adaptive culture can be a significant competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Transactional Factors
The Burke-Litwin Model includes several key transactional factors that shape everyday operations and interactions within an organization. These elements directly impact how work gets done and influence employee performance at a practical level.
Management Practices
Management practices involve the day-to-day behaviors and actions of managers as they work with their teams. This includes how managers communicate, delegate tasks, provide feedback, and support their employees.
Effective managers set clear expectations and goals for their team members. They offer regular coaching and mentoring to help employees develop their skills.
Good management practices also involve fair and consistent decision-making. Managers should strive to create a positive work environment where team members feel valued and motivated.
Regular team meetings and one-on-one check-ins help keep everyone aligned and informed. Managers who practice active listening and open communication tend to build stronger relationships with their teams.
Structure
Organizational structure defines how work is divided, coordinated, and supervised within a company. It outlines reporting relationships, decision-making authority, and communication channels.
Common structures include:
- Hierarchical
- Flat
- Matrix
- Divisional
- Network
Your company’s structure affects how information flows and how quickly decisions can be made. A flatter structure may promote more collaboration and faster decision-making, while a hierarchical one might offer clearer lines of authority.
The right structure depends on your organization’s size, industry, and goals. It should support your business strategy and help employees work efficiently.
Systems
Systems refer to the processes, procedures, and tools used to carry out work within your organization. These include:
- Information systems
- HR processes
- Financial systems
- Quality control measures
- Communication platforms
Effective systems help streamline operations and ensure consistency across your organization. They support decision-making by providing accurate and timely data.
Your HR systems, for example, might include performance management tools, training programs, and recruitment processes. Financial systems track budgets, expenses, and revenue.
Well-designed systems can boost productivity and reduce errors. They should be user-friendly and align with your company’s goals and culture.
Work Unit Climate
Work unit climate describes the shared perceptions and attitudes within a specific team or department. It’s about how it feels to work in a particular group.
Factors that shape work unit climate include:
- Leadership style of the immediate supervisor
- Team dynamics and relationships
- Workload and resources
- Recognition and rewards
- Physical work environment
A positive work climate can boost morale, productivity, and job satisfaction. Teams with a good climate often have better collaboration and lower turnover rates.
To improve your work unit climate, focus on clear communication, fair treatment, and addressing conflicts promptly. Encourage team-building activities and create opportunities for social interaction.
Tasks and Skills
This factor focuses on the specific job requirements and the abilities needed to perform them effectively. It’s about matching the right skills to the right tasks.
Key considerations include:
- Job design and responsibilities
- Required technical skills
- Soft skills like communication and teamwork
- Training and development opportunities
Well-defined tasks help employees understand their roles clearly. This can lead to better performance and job satisfaction.
Regular skill assessments can help you identify gaps in your team’s abilities. You can then provide targeted training or hire new talent to fill these gaps.
Consider creating detailed job descriptions that outline both tasks and required skills. This helps in recruitment and performance evaluation.
Individual Needs and Values
This factor recognizes that each employee has unique motivations, goals, and beliefs. Understanding and addressing these can significantly impact job satisfaction and performance.
Key aspects include:
- Personal career aspirations
- Work-life balance preferences
- Cultural and ethical values
- Recognition and reward preferences
By aligning job roles with individual needs and values, you can boost engagement and retention. This might involve offering flexible work arrangements or personalized development plans.
Regular one-on-one meetings can help managers understand their team members’ individual needs. Employee surveys and feedback sessions are also valuable tools.
Remember, what motivates one employee may not work for another. A tailored approach often yields better results.
Motivation
Motivation drives employee behavior and performance. It’s influenced by both intrinsic factors (personal satisfaction, sense of achievement) and extrinsic factors (rewards, recognition).
Strategies to boost motivation include:
- Setting clear, achievable goals
- Providing regular feedback and recognition
- Offering opportunities for growth and development
- Ensuring fair compensation and benefits
A well-designed motivation system can significantly improve productivity and job satisfaction. It should align with your organization’s goals and culture.
Consider implementing a mix of short-term incentives (like bonuses) and long-term rewards (such as career advancement opportunities). Regular check-ins can help you gauge employee motivation levels and address any issues promptly.
Remember, different employees may be motivated by different factors. A flexible approach that caters to individual preferences often works best.
Organizational Performance
The Burke-Litwin Model looks at how different factors affect an organization’s results. It helps managers understand what drives success and where to focus improvement efforts.
Productivity and Profitability
Productivity measures how efficiently your organization uses resources. It’s about getting more output from your inputs. You can track productivity by looking at things like units produced per hour or sales per employee.
Profitability shows if you’re making money. It’s the difference between your revenue and costs. Key profitability metrics include:
- Gross profit margin
- Net profit margin
- Return on investment (ROI)
To boost both, you might:
- Streamline processes
- Invest in new technology
- Train employees
- Reduce waste
Remember, productivity doesn’t always mean higher profits. You need to balance efficiency with quality and customer satisfaction.
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics help you measure progress toward goals. They show if you’re on track or need to adjust. Good metrics are:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
Common types include:
- Financial: Revenue growth, cost reduction
- Customer: Satisfaction scores, retention rates
- Internal: Process efficiency, quality control
- Learning/Growth: Employee skills, innovation rates
Use a mix of leading (predict future performance) and lagging (show past results) indicators. This gives a fuller picture of your organization’s health.
Employee Performance
Your employees drive organizational success. Their performance affects productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction. To improve employee performance:
- Set clear expectations
- Provide regular feedback
- Offer training and development
- Recognize and reward good work
Use performance reviews to discuss goals and progress. But don’t wait for annual reviews – give feedback often.
Consider using a performance management system to track employee goals, skills, and achievements. This can help you identify top performers and areas for improvement.
Overall Performance
Overall performance is how well your organization meets its goals. It’s a big-picture view that combines all aspects of your business. To assess overall performance, you might use:
- Balanced Scorecard: Looks at financial, customer, internal, and learning/growth perspectives
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Critical metrics aligned with your strategy
- Benchmarking: Comparing your results to industry standards or competitors
Regular performance reviews help you spot trends and make adjustments. You can use tools like dashboards to visualize data and track progress over time.
Remember, performance is about more than just numbers. Consider factors like employee satisfaction, innovation, and corporate social responsibility too. These can affect your long-term success.
Change Management Process
The Burke-Litwin Model provides a framework for managing organizational change effectively. It emphasizes the importance of understanding change initiatives, identifying drivers, implementing processes, and focusing on continuous improvement.
Understanding Change Initiatives
To manage change successfully, you need to grasp the nature of the change initiative. Transformational change affects the organization’s culture and mission, while transactional change focuses on day-to-day operations.
Identify the type of change you’re dealing with. This will help you choose the right approach and resources.
Consider the impact on different levels of the organization. Will it affect leadership, structure, or individual roles?
Clarify the goals of the change initiative. What outcomes do you expect? How will you measure success?
Change Drivers and Input
Change doesn’t happen in a vacuum. External and internal factors drive organizational change.
External drivers might include:
- Market competition
- New technologies
- Economic conditions
- Regulatory changes
Internal drivers could be:
- Employee feedback
- Performance issues
- New leadership
- Strategic shifts
Gather input from various stakeholders. This includes employees, managers, and customers. Their perspectives can provide valuable insights and help you anticipate challenges.
Use surveys, interviews, or focus groups to collect this input. This data will inform your change management strategy.
Change Process and Implementation
Once you understand the change and its drivers, it’s time to implement. Start by creating a detailed action plan.
Your plan should include:
- Clear objectives
- Timelines
- Resource allocation
- Communication strategy
- Training needs
Assign responsibilities to team members. Make sure everyone knows their role in the change process.
Communicate the change effectively. Be transparent about the reasons for change and expected outcomes. Address concerns and questions promptly.
Provide necessary training and support. This helps employees adapt to new processes or systems.
Monitor progress regularly. Be prepared to adjust your plan if needed.
Continuous Improvement
Change management doesn’t end with implementation. It’s an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement.
Regularly assess the effectiveness of your change initiatives. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress.
Seek feedback from employees and stakeholders. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement.
Be open to making adjustments. If certain aspects of the change aren’t working, be willing to modify your approach.
Celebrate successes along the way. This boosts morale and reinforces the positive aspects of change.
Foster a culture of innovation and adaptability. Encourage employees to suggest improvements and embrace change as a normal part of organizational life.
Impact on Employees

The Burke-Litwin Model highlights how organizational changes affect employees. It shows the connection between workplace factors and employee outcomes.
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement is a key focus of the Burke-Litwin Model. It looks at how changes in the work environment impact employee involvement.
When leaders make changes, it can increase or decrease engagement. For example, clearer communication often boosts engagement. Employees feel more connected to the company’s goals.
Changes in job roles or team structures may affect engagement too. You might see employees become more invested if given new responsibilities. Or they could disengage if they feel their role is less important after a change.
The model suggests monitoring engagement levels during change. This helps you spot issues early and make adjustments.
Employee Motivation
Motivation is another important employee factor in the Burke-Litwin Model. It looks at what drives employees to perform well.
Changes in leadership style can greatly impact motivation. A new manager with a more inspiring approach might boost motivation. On the flip side, a shift to a more controlling style could lower it.
Adjustments to reward systems also affect motivation. You might see increased effort if bonuses are tied to specific goals. Or motivation could drop if rewards are cut.
The model suggests considering how each change might affect what drives your employees. This helps you make changes that keep motivation high.
Employee Satisfaction
Employee satisfaction is a crucial element in the Burke-Litwin Model. It focuses on how content employees are with their work and workplace.
Changes in company culture can greatly impact satisfaction. A shift towards more work-life balance might increase satisfaction. Or a move to a more competitive culture could lower it for some.
Workplace policies and practices also play a role. New flexible work options might boost satisfaction. But stricter rules could have the opposite effect.
The model advises tracking satisfaction during changes. This helps you understand how your decisions affect employee happiness.
Individual Performance
Individual performance is a key outcome in the Burke-Litwin Model. It looks at how organizational changes impact each employee’s work quality and output.
Changes in tools or technology can affect performance. New software might improve efficiency for some. But it could slow down others who struggle to adapt.
Shifts in team dynamics also impact individual performance. A more collaborative approach might boost some employees’ output. Others might perform better with more independence.
The model suggests monitoring individual performance closely during changes. This helps you spot who needs extra support or training.
Individual Skills
The Burke-Litwin Model also considers how organizational changes affect individual skills. It looks at skill development and utilization.
Changes in job roles often require new skills. You might see employees quickly develop new abilities when given challenging tasks. Or some might struggle if not given proper training.
Shifts in company strategy can also impact skills. A move towards more digital services might require employees to build tech skills. This could lead to rapid skill growth for some.
The model advises considering skill needs when planning changes. This helps you prepare employees for new demands and opportunities.
Evaluating Organizational Success
The Burke-Litwin Model provides a framework for assessing how well a company is doing. It looks at different parts of an organization and how they affect success.
Measuring Performance Improvement
To gauge how well your organization is doing, you need to track key metrics. These might include sales numbers, customer satisfaction scores, or employee productivity rates.
Set clear goals for each area you want to improve. Then, use tools like balanced scorecards or key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress.
Regular check-ins are important. Review your data monthly or quarterly to spot trends. This helps you see if your changes are working.
Remember to celebrate wins, big and small. When teams see their hard work paying off, it boosts morale and drives further improvement.
Relevance of Internal Factors
Your company’s inner workings play a big role in its success. The Burke-Litwin Model highlights several key internal factors that affect performance.
Leadership style is crucial. How your managers guide their teams can make or break projects. Good leaders inspire and motivate.
Company culture also matters a lot. A positive work environment leads to happier, more productive employees.
Look at your organizational structure too. Is it helping or hindering work flow? Sometimes, reshaping teams or departments can boost efficiency.
Don’t forget about individual skills and motivation. Investing in training and development can pay off big time in the long run.
Adapting to Economic and Technological Changes
The business world is always changing. Your company needs to keep up to stay successful. The Burke-Litwin Model recognizes external factors as key drivers of change.
Keep an eye on economic trends. They can affect your market and customer behavior. Be ready to adjust your strategies if needed.
Embrace new technologies. They can help you work smarter and faster. But choose wisely – not every new tool is right for every business.
Stay ahead of industry shifts. What worked yesterday might not work tomorrow. Be willing to try new approaches when the market demands it.
Build a culture of flexibility in your team. When people are open to change, your whole organization becomes more adaptable.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Burke-Litwin model helps organizations understand and manage change. It considers many factors that affect how a company works and performs. Let’s look at some common questions about this model.
What is the relationship between the Burke-Litwin model and organizational development?
The Burke-Litwin model is a key tool in organizational development. It helps you see how different parts of your company connect and affect each other.
This model shows you where to focus when making changes. It helps you plan and carry out improvements in your organization.
How can the Burke-Litwin model be applied in the context of organizational change?
You can use the Burke-Litwin model to guide change in your company. First, look at each part of the model to see where changes are needed.
Then, make a plan that covers all these areas. As you make changes, keep checking how they affect other parts of your organization.
What benefits does the Burke-Litwin model offer for organizational transformation?
The Burke-Litwin model gives you a full picture of your organization. It helps you see how changes in one area can affect others.
This model also helps you predict outcomes of changes. It lets you plan more carefully and avoid surprise problems.
How does the Burke-Litwin model integrate with existing theories of organizational change?
The Burke-Litwin model fits well with other change theories. It adds to them by showing how different parts of an organization are linked.
This model also considers both big and small changes. It helps you see how they all work together to affect your company.
What factors are considered in the Burke-Litwin model when analyzing organizational performance?
The Burke-Litwin model looks at many factors. These include your company’s mission, leadership, and culture.
It also considers your work processes, systems, and skills. The model even looks at things like motivation and individual needs.
Can you provide an example of the Burke-Litwin model implemented within an organizational setting?
A company might use the Burke-Litwin model when changing its customer service approach. They would look at how this change affects their mission, culture, and systems.
They would also consider how it impacts individual jobs and skills. This helps them make a complete plan for the change.