Change management is a critical aspect of organizational development and success. It involves implementing strategies and processes to effectively navigate and adapt to change within an organization. In this article, we will explore the concept of change management, its importance, and the various change management models available for organizations to consider.
We’ll delve into well-known models such as:
- Lewin’s Change Management Model
- Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
- McKinsey 7-S Change Model
- ADKAR Change Management Model
- Prosci’s ADKAR Model
- Bridges’ Transition Model
- Kotter’s Change Management Model
- Satir Change Management Model
- Deming Cycle Change Management Model
- Nudge Theory Change Management Model
We will also discuss which change management model may be best suited for different organizational needs and provide insights on how to select the right model for your organization.
Key Takeaways:
- A successful change management model is essential for navigating organizational changes.
- There are various change management models to choose from, each with its own unique approach and benefits.
- When selecting a change management model, consider your organization’s specific needs and goals to ensure a successful implementation.
What Is Change Management?
Change management is the structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from a current state to a desired future state to achieve the anticipated business outcome.
This approach aims to facilitate organizational changes in the most efficient and smooth manner possible. Change management encompasses a range of actions and initiatives, including strategic planning, communication, and employee engagement, to minimize resistance and promote successful implementation.
With various methodologies such as Kotter’s 8-step process or ADKAR model, it provides a roadmap for executing change. Employee involvement during the change process is paramount, as it fosters a sense of ownership and commitment, ultimately leading to higher acceptance and smoother transition.
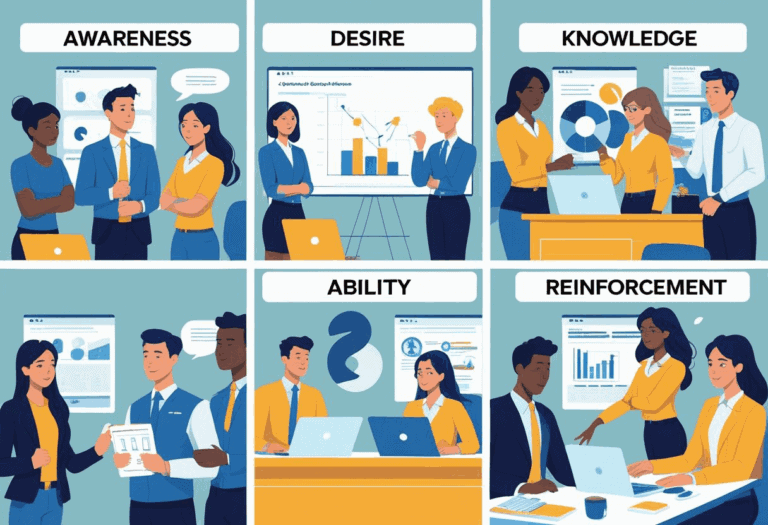
Organizations’ transition through stages of change, including awareness, desire, knowledge, ability, and reinforcement, is crucial. Managing these stages effectively can mitigate disruptions and uncertainties, ensuring a more seamless shift to the new state.
Why Is Change Management Important?
Change management is crucial for organizations as it facilitates successful transitions, minimizes resistance, and ensures effective implementation of new strategies or processes.
Effective change management plays a pivotal role in steering organizations through the turbulent waters of transformation. It not only fosters a smooth transition from the old ways to the new but also directly addresses the inevitable employee resistance that accompanies change.
By harnessing the principles of change management, organizations can proactively identify potential hurdles and develop tailored strategies to overcome them. It provides a structured framework for the seamless implementation of change initiatives, ensuring that the intended changes take root and yield the desired outcomes.
What Are the Different Change Management Models?
Various change management models offer structured frameworks to guide organizations through the process of change, each with its distinct approach and principles.
Some well-known change management models include:
Kotter’s 8-step model focuses on creating a sense of urgency, forming a powerful coalition, and enabling short-term wins, among other steps.
Lewin’s Change Management Model emphasizes the unfreezing, changing, and refreezing stages, while the ADKAR Model by Prosci focuses on awareness, desire, knowledge, ability, and reinforcement.
The McKinsey 7-S Model emphasizes strategy, structure, systems, style, staff, skills, and shared values. Each model holds unique methodologies and principles that offer valuable guidance to organizations undergoing change.
Which Change Management Model Should I use?
Navigating the complexities of organizational change can be challenging, but choosing the right change management model doesn’t have to be.
Our tool, ModelMatch Pro, is designed to help you identify the most suitable framework for your specific needs and goals.
Whether you’re dealing with large-scale transformations or incremental adjustments, ModelMatch Pro provides tailored recommendations to ensure a smooth and effective transition.
Discover the perfect model to guide your change initiatives and drive lasting success.
Lewin’s Change Management Model
Lewin’s Change Management Model, developed by Kurt Lewin, is a foundational approach that emphasizes the stages of unfreezing, changing, and refreezing to facilitate successful organizational transitions.

Unfreezing involves preparing the organization for change by addressing change resistance, creating awareness and understanding the need for change. The changing stage focuses on implementing the actual changes while involving employee engagement and encouraging new attitudes and behaviors.
The refreezing stage aims to solidify the changes, making them a part of the organizational culture and ensuring sustainable change by aligning processes, systems, and behaviors.
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model, proposed by Dr. John P. Kotter, provides a comprehensive framework for successful change implementation, encompassing steps such as creating a sense of urgency, forming a powerful coalition, and anchoring changes in corporate culture.
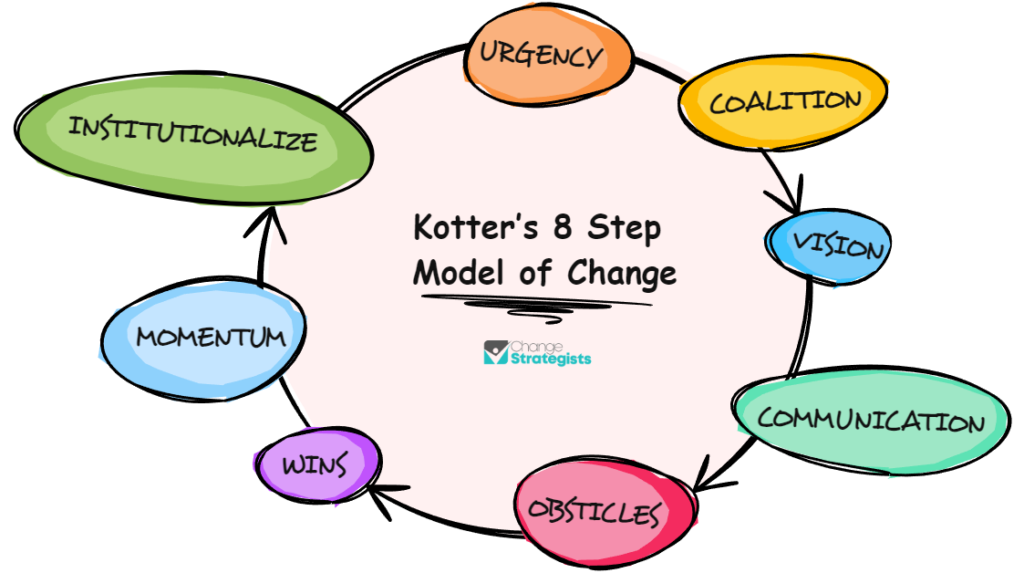
It begins with the first step, creating a sense of urgency, which emphasizes the importance of communicating the need for change effectively throughout the organization. This step enables leaders to galvanize the workforce toward a common goal, fostering motivation and commitment.
The subsequent step of forming a powerful coalition focuses on building a team of influential individuals who can drive the change effort and support its implementation. This coalition should comprise individuals with diverse skills, expertise, and perspectives to ensure holistic decision-making and effective change management.
The step of anchoring changes in corporate culture underscores the significance of integrating new behaviors, practices, and norms within the organization’s cultural fabric. This step entails aligning the change with the company’s values, norms, and beliefs, thus ensuring its sustainability and long-term success.
McKinsey 7-S Change Model
The McKinsey 7-S Change Model, developed by McKinsey & Company, focuses on seven interdependent factors, including strategy, structure, systems, and shared values, to enable organizational change and effectiveness.
These seven elements of the model work together to create a holistic view of an organization and its ability to achieve strategic objectives. The strategy component emphasizes the organization’s plan for reaching its goals, while the structure element looks at the organization’s hierarchy and reporting relationships.
The systems element examines the daily processes and routines that support the work of the organization, and the shared values aspect focuses on the core beliefs and behaviors that are encouraged and rewarded within the organization.
ADKAR Change Management Model
The ADKAR Change Management Model, developed by Prosci, outlines five key elements – awareness, desire, knowledge, ability, and reinforcement – essential for driving successful change at the individual level within organizations.
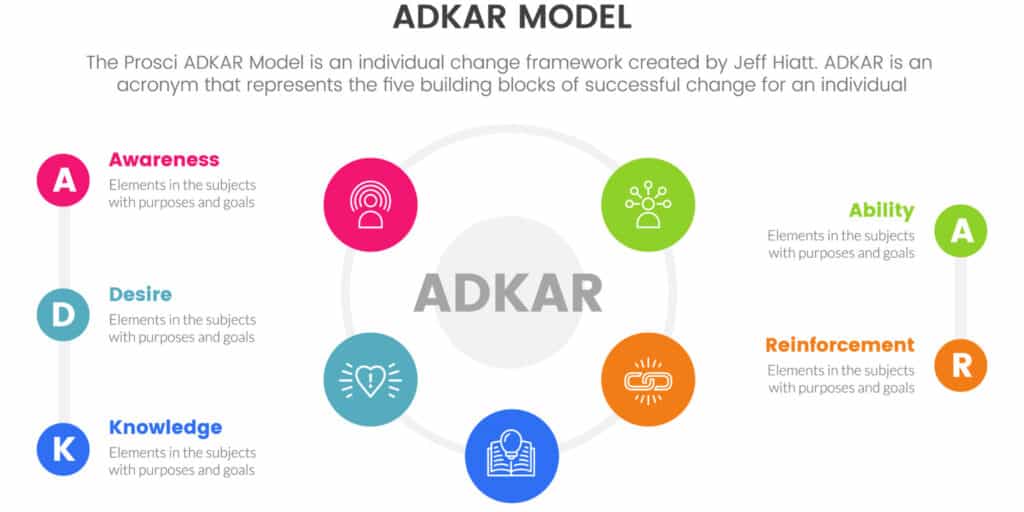
At the heart of the ADKAR model is the emphasis on the individual’s transition during organizational change, acknowledging their unique responses and challenges.
Awareness marks the starting point, where individuals comprehend the need for change and its potential impacts. Subsequently, desire delves into the personal motivation for embracing the change, while knowledge entails equipping individuals with the essential information and understanding.
The ability phase revolves around give the power toing individuals with the necessary skills and support to implement the change effectively. Finally, reinforcement plays a crucial role in sustaining the change by recognizing and rewarding desired behaviors. By addressing these critical components, organizations can foster a culture of adaptability and enhance employee engagement.”
Prosci’s ADKAR Model
Prosci’s ADKAR Model provides a structured approach to understanding and managing individual change, ensuring that employees are effectively equipped to navigate through transitions and embrace new ways of working.
This model focuses on the individual transitions by identifying the change readiness as well as the elements of awareness, desire, knowledge, ability, and reinforcement. By breaking down the process into these components, it helps organizations address the human side of change, supporting employees in their shift from uncertainty to confidence, resistance to acceptance, and ineffectiveness to proficiency. It encourages a proactive approach to employee transition, promoting a culture of adaptability and resilience in the face of organizational change.
Bridges’ Transition Model
Bridges’ Transition Model, developed by William Bridges, focuses on the psychological transition experienced by individuals during change, emphasizing the importance of navigating the endings, neutral zone, and new beginnings within the change process.
This model proposes that when individuals encounter change, they first experience endings, which involves letting go of the old ways, habits, and patterns.
This stage is often marked by a sense of loss, uncertainty, and emotional distress. Subsequently, they enter the neutral zone where the old is gone, but the new is not yet fully operational.
This phase involves dealing with ambiguity, disorientation, and a sense of being in-between. Individuals move towards new beginnings, embracing fresh perspectives, aligning with new goals, and integrating new practices. The model asserts that understanding and addressing the psychological implications of change are vital for successful transition.
Satir Change Management Model
The Satir Change Management Model, developed by Virginia Satir, emphasizes the human aspects of change and the impact on individuals, addressing emotional responses, growth, and transformation during the change process.
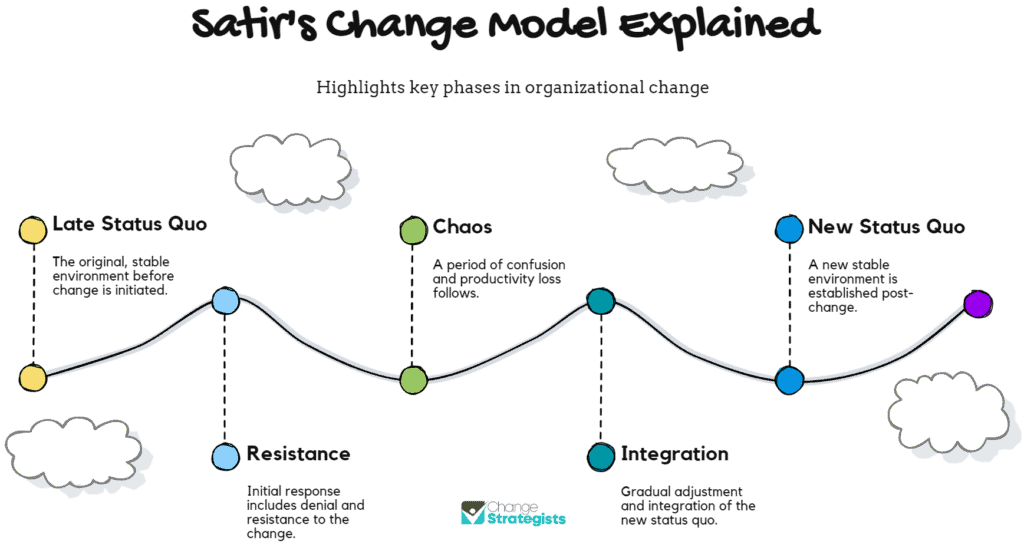
One of the key tenets of the Satir Change Management Model revolves around the acknowledgment of emotional responses to change. It recognizes that individuals experience various emotions, such as fear, resistance, or anxiety, during periods of transition.
The model encourages personal growth by fostering an environment that supports individuals in understanding, processing, and coping with these emotions.
It focuses on individual transformation within the context of organizational change, aiming to tap into the potential for personal development and enhanced resilience.
This emphasis on human emotions and personal growth distinguishes the Satir Change Management Model from more traditional, purely structural approaches to change management.
Deming Cycle Change Management Model
The Deming Cycle Change Management Model, attributed to Dr. Williams Edwards Deming, revolves around the continuous improvement process known as Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA), ensuring iterative and incremental changes within organizations.
The model emphasizes the significance of constantly evaluating and refining processes to enhance organizational efficiency. By focusing on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, it creates a structured approach to managing change and innovation.
This iterative method involves planning a change, implementing it, then evaluating the outcomes before fully adopting it.
This systematic approach enables organizations to adapt to evolving conditions and continuously improve their operations.
Nudge Theory Change Management Model
Nudge Theory, developed by Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein, presents a behavioral economics approach to change management, focusing on indirect suggestions and positive reinforcement to influence decision-making and behavioral change.

This theory is grounded in the understanding of how individuals make decisions and the influences that shape their behaviors.
By leveraging behavioral economics principles, Nudge Theory aims to guide individuals towards desired choices and actions without restricting their freedom of choice.
It emphasizes the power of subtle, indirect influences in steering individuals and organizations towards beneficial outcomes.
Through positive reinforcement, it seeks to encourage and maintain changes in behavior, making it a valuable tool in driving organizational change.
Which Change Management Model Is Best?
There is no one-size-fits-all approach, and the effectiveness of a change management model depends on the specific organizational context, type of change, and the readiness of employees to embrace the change.
Organizations need to carefully assess their unique organizational culture, communication channels, existing hierarchies, and the level of stakeholder involvement to determine the most suitable change management model.
A change model that aligns with the organization’s values and vision is more likely to gain acceptance and facilitate successful implementation.
Taking into account the degree of uncertainty associated with the change, the pace at which the change needs to be implemented, and the level of employee autonomy within the organization are crucial factors in selecting an appropriate change management model.
How to Choose the Right Change Management Model for Your Organization?
Selecting the appropriate change management model involves assessing the nature of the change, organizational dynamics, employee engagement, and aligning the model with the strategic objectives of the organization.
Understanding the nature of the change is crucial as it helps in determining the urgency and impact of the change, whether it’s incremental or transformational. Evaluating the organizational dynamics involves analyzing the existing structures, processes, and systems to gauge their readiness for change.
Employee engagement plays a key role in the successful adoption of the chosen change management model, emphasizing the need for effective communication, involvement, and support throughout the process. Aligning the model with the strategic objectives ensures that the change initiatives contribute to the overall organizational goals and vision.
What Are the Steps for Implementing a Change Management Model?
The implementation of a change management model entails several key steps, including creating a sense of urgency, communicating the change vision, give the power toing employees, and sustaining the change momentum.
Establishing a sense of urgency is crucial to gaining the buy-in of employees and stakeholders for the proposed change. This can be achieved by presenting compelling data and trends that highlight the necessity for change, thereby motivating people to support the initiative.
Once the urgency is established, communicating the change vision becomes paramount. It involves articulating the desired future state, addressing potential concerns, and outlining the benefits of the change.
Empowering employees through involvement in decision-making and providing them with the necessary resources and support fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the change. Sustaining the change momentum requires continuous reinforcement of the new behaviors and practices, celebrating milestones, and addressing any setbacks effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best change management model for my organization?
The best change management model for your organization will depend on various factors such as the nature of your business, organizational culture, and the type of changes you want to implement. It is essential to research and carefully consider different models to find the one that best fits your organization.
What are the key components of a successful change management model?
A successful change management model should include elements such as communication, stakeholder engagement, clear goals and objectives, a structured approach, and monitoring and evaluation. These components help ensure that the change is well-planned and executed efficiently.
How can I effectively communicate the change to my employees?
Communication is a vital aspect of change management. To effectively communicate the change, you should use multiple channels such as email, meetings, and one-on-one conversations. It is also crucial to be transparent and address any concerns or questions your employees may have.
What are the benefits of using a change management model?
Change management models provide a structured approach to managing change, which can increase the chances of successful implementation. They also promote stakeholder engagement, communication, and alignment, leading to a smoother transition and reduced resistance to change.
Can I customize a change management model to suit my organization’s needs?
Yes, change management models can be customized to fit the specific needs and culture of your organization. It is essential to understand the principles and framework of the model before making any modifications to ensure its effectiveness.
How often should I review and update my change management model?
Change is a continuous process, and as such, it is important to regularly review and update your change management model. This will help ensure its relevance and effectiveness in managing change within your organization. It is recommended to review the model after each change initiative or every 6-12 months.